Psoralen Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Human Extravillous Trophoblast Derived HTR-8/Svneo Cells in vitro by NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 35462898
- PMCID: PMC9024043
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.804400
Psoralen Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Human Extravillous Trophoblast Derived HTR-8/Svneo Cells in vitro by NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
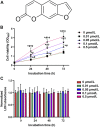
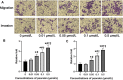
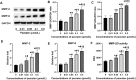
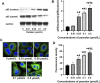
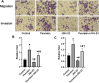
Recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) is a kind of pathological pregnancy, and abnormal function of trophoblast cells may be related to a variety of pregnancy complications including RSA. Psoralen is an effective ingredient extracted from Cullen corylifolium (L.) Medik. with multiple bioactivities mainly including anti-osteoporotic, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and estrogen-like effects. However, the exact role of psoralen on trophoblast invasiveness has not been investigated thus far. In the present study, the effects of psoralen on the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of HTR-8/SVneo cells were evaluated by the CCK-8 and Transwell assays. The expression patterns of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)/p65 and metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 were characterized by further experiments including real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and Western blot. Indirect immunofluorescence was applied to track the NF-κB p65 translocation. Herein, we found that cell viability and invasive ability were promoted by psoralen in a concentration-dependent manner. Psoralen concentration-dependently enhanced both MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression and their activity of HTR-8/SVneo cells. Additionally, we observed accelerated nuclear accumulation and enhanced nuclear translocation of p65 in the presence of psoralen. Furthermore, invasiveness enhancement of psoralen on HTR-8/SVneo cells was partly eliminated by a NF-κB pathway inhibitor. Thus, our findings suggest that psoralen may serve as a potential repurpose drug candidate that can be used to induce migration and invasion of trophoblast cells through strengthening the NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: NF-κB pathway; human extravillous trophoblast; invasion; migration; proliferation; psoralen.
Copyright © 2022 Qi, Lu, Fu, Lv and Hou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brouillet S., Murthi P., Hoffmann P., Salomon A., Sergent F., De Mazancourt P., et al. (2013). EG-VEGF Controls Placental Growth and Survival in Normal and Pathological Pregnancies: Case of Fetal Growth Restriction (FGR). Cell Mol. Life Sci. 70, 511–525. 10.1007/s00018-012-1141-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

