Ginsenoside Compound K Enhances Fracture Healing via Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis
- PMID: 35462912
- PMCID: PMC9020191
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.855393
Ginsenoside Compound K Enhances Fracture Healing via Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis
Abstract
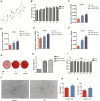
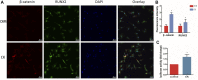
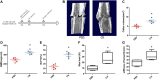
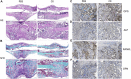
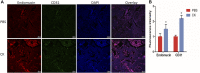
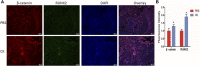
Fractures have an extraordinarily negative impact on an individual's quality of life and functional status, particularly delayed or non-union fractures. Osteogenesis and angiogenesis are closely related to bone growth and regeneration, and bone modeling and remodeling. Recently Chinese medicine has been extensively studied to promote osteogenic differentiation in MSCs. Studies have found that Ginseng can be used as an alternative for tissue regeneration and engineering. Ginseng is a commonly used herbal medicine in clinical practice, and one of its components, Ginsenoside Compound K (CK), has received much attention. Evidence indicates that CK has health-promoting effects in inflammation, atherosclerosis, diabetics, aging, etc. But relatively little is known about its effect on bone regeneration and the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms. In this study, CK was found to promote osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (rBMSCs) by RT-PCR and Alizarin Red S staining in vitro. Mechanistically, we found CK could promote osteogenesis through activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by immunofluorescence staining and luciferase reporter assay. And we also showed that the tube formation capacity of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) was increased by CK. Furthermore, using the rat open femoral fracture model, we found that CK could improve fracture repair as demonstrated by Micro-CT, biomechanical and histology staining analysis. The formation of H type vessel in the fracture callus was also increased by CK. These findings provide a scientific basis for treating fractures with CK, which may expand its application in clinical practice.
Keywords: CK; Wnt/β-catenin; angiogenesis; fracture healing; osteogenesis.
Copyright © 2022 Ding, Gu, Zhou, Wang, Zhang, Wu, Zou, Zhao, Gao and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EGFL6 regulates angiogenesis and osteogenesis in distraction osteogenesis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jul 22;12(1):415. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02487-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34294121 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of SERPINB2 enhances the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Oct 7;12(1):525. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02581-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34620242 Free PMC article.
-
Irisin promotes fracture healing by improving osteogenesis and angiogenesis.J Orthop Translat. 2022 Sep 24;37:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.07.006. eCollection 2022 Nov. J Orthop Translat. 2022. PMID: 36196152 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Mechanisms of Ginsenoside Compound K: A Review.Diseases. 2025 May 5;13(5):143. doi: 10.3390/diseases13050143. Diseases. 2025. PMID: 40422575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A narrative review of the pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(4):234. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-501. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35280413 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Compounds Involved in the Bone Regeneration Process and Their Innovative Administration: A Systematic Review.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 22;12(10):2055. doi: 10.3390/plants12102055. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37653972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Gellan Gum, Polyethylene Glycol, Hydroxyapatite Composite Scaffold with the Addition of Ginseng Derived Compound K with Possible Applications in Bone Regeneration.Gels. 2024 Apr 10;10(4):257. doi: 10.3390/gels10040257. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667676 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Validation of Antiobesogenic and Osteoprotective Efficacy of Ginsenoside CK via Targeting Lipid and Atherosclerosis Pathways.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 31;15(1):41. doi: 10.3390/life15010041. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39859981 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Research on the Role of Phytochemicals from Ginseng in Management of Osteosarcoma, Osteoporosis, and Osteoarthritis.Nutrients. 2025 Jun 1;17(11):1910. doi: 10.3390/nu17111910. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside compound-K attenuates OVX-induced osteoporosis via the suppression of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and oxidative stress.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2023 Nov 9;13(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s13659-023-00405-z. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2023. PMID: 37940733 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

