Management of Acute Kidney Injury and Extracorporeal Blood Purification Therapies During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Italian SIN-SIAARTI Joint Survey (and Recommendations for Clinical Practice)
- PMID: 35463000
- PMCID: PMC9021595
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.850535
Management of Acute Kidney Injury and Extracorporeal Blood Purification Therapies During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Italian SIN-SIAARTI Joint Survey (and Recommendations for Clinical Practice)
Abstract
Background and aim: The novel coronavirus disease 2019 remains challenging. A large number of hospitalized patients are at a high risk of developing AKI. For this reason, we conducted a nationwide survey to assess the incidence and management of AKI in critically ill patients affected by the SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Methods: This is a multicenter, observational, nationwide online survey, involving the Italian Society of Nephrology and the critical care units in Italy, developed in partnership between the scientific societies such as SIN and SIAARTI. Invitations to participate were distributed through emails and social networks. Data were collected for a period of 1 week during the COVID-19 pandemic.
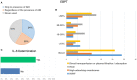
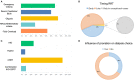
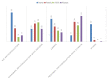
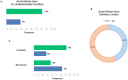
Results: A total of 141 responses were collected in the SIN-SIAARTI survey: 54.6% from intensivists and 44.6% from nephrologists. About 19,000 cases of COVID-19 infection have been recorded in hospitalized patients; among these cases, 7.3% had a confirmed acute kidney injury (AKI), of which 82.2% were managed in ICUs. Only 43% of clinicians routinely used the international KDIGO criteria. Renal replacement therapy (RRT) was performed in 628 patients with continuous techniques used most frequently, and oliguria was the most common indication (74.05%). Early initiation was preferred, and RRT was contraindicated in the case of therapeutic withdrawal or in the presence of severe comorbidities or hemodynamic instability. Regional anticoagulation with citrate was the most common choice. About 41.04% of the interviewed physicians never used extracorporeal blood purification therapies (EBPTs) for inflammatory cytokine or endotoxin removal. Moreover, 4.33% of interviewed clinicians used these techniques only in the presence of AKI, whereas 24.63% adopted them even in the absence of AKI. Nephrologists made more use of EBPT, especially in the presence of AKI. HVHF was never used in 58.54% of respondents, but HCO membranes and adsorbents were used in more than 50% of cases.
Conclusion: This joint SIN-SIAARTI survey at the Italian Society of Nephrology and the critical care units in Italy showed that, during the COVID-19 pandemic, there was an underestimation of AKI based on the "non-use" of common diagnostic criteria, especially by intensivists. Similarly, the use of specific types of RRT and, in particular, blood purification therapies for immune modulation and organ support strongly differed between centers, suggesting the need for the development of standardized clinical guidelines.
Keywords: COVID-19; acute kidney injury; blood purification; critical care; renal replacement therapy; surveys and questionnaires.
Copyright © 2022 De Rosa, Marengo, Romagnoli, Fiorentino, Fanelli, Fiaccadori, Brienza, Morabito, Pota, Valente, Grasselli, Messa, Giarratano and Cantaluppi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracorporeal blood purification therapies for sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: expert opinion from the SIAARTI-SIN joint commission.J Nephrol. 2023 Sep;36(7):1731-1742. doi: 10.1007/s40620-023-01637-5. Epub 2023 Jul 13. J Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37439963 Free PMC article.
-
Regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) in critically ill patients undergoing renal replacement therapy (RRT): expert opinion from the SIAARTI-SIN joint commission.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2023 Mar 31;3(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s44158-023-00091-w. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 37386664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
International Survey on the Management of Acute Kidney Injury and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapies: Year 2018.Blood Purif. 2019;47(1-3):113-119. doi: 10.1159/000493724. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Blood Purif. 2019. PMID: 30269144
-
Nutrition support for critically ill patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: the Italian SIAARTI survey.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2022 Aug 9;2(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s44158-022-00063-6. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 37386650 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and the Kidney: Should Nephrologists Care about COVID-19 rather than Maintaining Their Focus on Renal Patients?Contrib Nephrol. 2021;199:229-243. doi: 10.1159/000517752. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Contrib Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34344017 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Update on persistent acute kidney injury in critical illnesses.Clin Kidney J. 2023 May 11;16(11):1813-1823. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad107. eCollection 2023 Nov. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 37915904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 outcomes in patients with a history of immune-mediated glomerular diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 12;14:1228457. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1228457. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37767096 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: COVID-19 Related Kidney Disease: From Epidemiology to Clinical Management.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 28;9:956409. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.956409. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35836943 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Extracorporeal blood purification therapies for sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: expert opinion from the SIAARTI-SIN joint commission.J Nephrol. 2023 Sep;36(7):1731-1742. doi: 10.1007/s40620-023-01637-5. Epub 2023 Jul 13. J Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37439963 Free PMC article.
-
Hemoperfusion Combined With Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in the Management of ARDS COVID-19 Patients: A Quasi-Experimental Study.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 1;8(4):e70571. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70571. eCollection 2025 Apr. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40177411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alenezi FK, Almeshari MA, Mahida R, Bangash MN, Thickett DR, Patel JM. Incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients with and without acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) during the first wave of COVID-19: a systematic review and Meta-Analysis. Ren Fail. (2021) 43:1621–33. 10.1080/0886022X.2021.2011747 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

