Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy With Adsorbing Filter oXiris in Acute Kidney Injury With Septic Shock: A Retrospective Observational Study
- PMID: 35463014
- PMCID: PMC9024201
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.789623
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy With Adsorbing Filter oXiris in Acute Kidney Injury With Septic Shock: A Retrospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background and objective: Sepsis/septic shock-associated acute kidney injury (S-AKI) is associated with prolonged kidney recovery and extremely high mortality. Extracorporeal blood purification therapy for the removal of endotoxin and cytokines might benefit patients with S-AKI. The purpose of this study was to compare the efficacy of adsorbing filter oXiris in the treatment of S-AKI.
Design setting participants and measurements: This was a retrospective observational study conducted from September 2017 to June 2020 in ICU. All patients received CRRT for ≥24 h. The primary outcomes were mortality. The secondary outcomes included cardiovascular SOFA score and vasoactive-inotropic score (VIS), the SOFA, the reduction of inflammatory mediators.
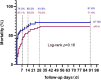
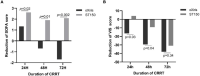
Results: A total of 136 septic shock patients with AKI were included. The interventional group (oXiris group; n = 70) received CRRT with endotoxic and cytokine adsorption function hemofilter (oXiris), while the control group (ST150 group; n = 66) was treated with the ST150 hemofilter. The early mortality in 7 and 14 days was significantly lower in oXiris group compared with ST150 group (7 days: 47.1 vs. 74.2%, P = 0.007; 14 days: 58.5 vs. 80.3%, P = 0.005), but the difference was not significant in 90-day mortality (71.4 vs. 81.8%, P = 0.160). Additionally, the reduction of the SOFA score in the oXiris group at 24, 48, and 72 h CRRT was significantly faster than that in the controlled group. Meanwhile, the reduction of VIS score in the oXiris group compared with the ST150 group at 24 and 48 h after the initiation of CRRT was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the decreases in procalcitonin were greater in the oXiris group than those in the ST150 group at 24, 48, and 72h after initiation of CRRT. Multivariate Cox regression model demonstrated that oXiris (vs. ST150) played a favorably important role in the prognosis of septic shock patients with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.500 (95% CI: 0.280-0.892; P = 019).
Conclusion: Although no difference was found in 90-day mortality, oXiris might reduce the short-term (<14-day) mortality compared with ST150 groups in septic shock with AKI. Further investigation in randomized controlled trials or high-quality prospective studies is warranted to validate the present findings.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; continuous renal replacement therapy; endotoxin; oXiris; sepsis/septic shock.
Copyright © 2022 Guan, Wang, Tang, Zhao, Wang, Zhang and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
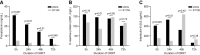

Similar articles
-
Continuous renal replacement therapy with adsorbing filter oXiris in the treatment of sepsis associated acute kidney injury: a single-center retrospective observational study.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Dec 18;25(1):456. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03897-0. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39696043 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Different Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Hemofilter in Patients with Septic Shock Complicated with Acute Renal Injury.Iran J Public Health. 2022 Oct;51(10):2317-2324. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v51i10.10990. Iran J Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36415800 Free PMC article.
-
Does Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with oXiris in Septic Shock Have Any Positive Impact? Single-Centre Experience with oXiris Therapy in Septic Shock Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 11;13(24):7527. doi: 10.3390/jcm13247527. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39768450 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with the Adsorbing Filter oXiris in Septic Patients: A Case Series.Blood Purif. 2019;47 Suppl 3:1-5. doi: 10.1159/000499589. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Blood Purif. 2019. PMID: 30982024 Review.
-
Septic shock after liver transplantation successfully treated with endotoxin and cytokine adsorption continuous renal replacement therapy: a case report and literature review.J Int Med Res. 2020 Jul;48(7):300060520940439. doi: 10.1177/0300060520940439. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32686965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Haemoadsorption Therapy on Short Term Mortality and Vasopressor Dependency in Severe Septic Shock with Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Dec 22;13(12):1233. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13121233. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766623 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with the oXiris Hemofilter on Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 13;11(22):6719. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226719. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Oxiris® Therapy on Cytokine Elimination after a LPS Infusion-An Experimental Animal Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 27;25(17):9283. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179283. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273234 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of hybrid blood purification for SA-AKI subtypes identified by CCL14: study protocol for a single-centre randomized controlled clinical trial.Trials. 2025 Aug 26;26(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s13063-025-09058-4. Trials. 2025. PMID: 40859313 Free PMC article.
-
A multicentre, randomised controlled clinical trial evaluating the effect of the adsorptive filter oXiris on haemodynamics in abdominal septic shock patients requiring continuous renal replacement therapy (Oxiris for Abdominal SEptic Shock study).BMJ Open. 2025 Jul 8;15(7):e094792. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-094792. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40633959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peters E, Antonelli M, Wittebole X, Nanchal R, Francois B, Sakr Y, et al. A worldwide multicentre evaluation of the influence of deterioration or improvement of acute kidney injury on clinical outcome in critically ill patients with and without sepsis at ICU admission: results from The Intensive Care Over Nations audit. Crit Care. (2018) 22:188. 10.1186/s13054-018-2112-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

