To Study the Role of Serum Homocysteine Levels and Ocular Involvement in Retinal Vasculitis
- PMID: 35463114
- PMCID: PMC8993952
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-021-00976-z
To Study the Role of Serum Homocysteine Levels and Ocular Involvement in Retinal Vasculitis
Abstract
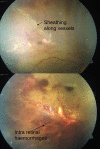
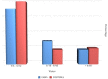
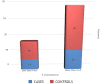
Idiopathic retinal vasculitis is a chronic disease of unknown aetiology which results in ocular morbidity in patients of productive age group. Homocysteine has been implicated in various ocular conditions like age-related macular degeneration, retinal vein occlusions, diabetic retinopathy, and optic nerve diseases. We conducted a study to investigate the relation between serum homocysteine levels and retinal vasculitis at a tertiary care centre in North India. In this case-control study, 32 cases and 64 controls were included and the duration was from June 2017 to March 2019. Serum homocysteine of cases and controls was detected by reflectance photometry using VITROS Chemistry Products HCY 2 (Homocysteine) and the normal range of serum homocysteine as per this method was 6.60 to 14.80 micro mol per litre. Our study found that of the total 32 retinal vasculitis patients, serum homocysteine was raised in 65.62% (21 cases out of 32) and in 70.31% of control group (45 out of 64). Chi square test results showed that there was no significant association found between S. homocysteine levels and Reticular vasculitis (P: 0.64). The two groups were comparable in terms of the age with mean ± SD in cases being 33.47 ± 8.336 years and controls being 35.16 ± 8.568 years with a P value of 0.37 being statistically insignificant. The data collected was analysed using SSPS-16 (Statistical Package for Social Sciences Version 16) software and test of association was Odd's ratio. Power of study was 80% and P < 0.05 is considered statistically significant. We found that there is no significant association between raised serum homocysteine and retinal vasculitis (with P < 0.64). Odds ratio was 0.80(0.33-1.99) implying that the cases and controls were statistically significantly different with respect to homocysteine levels.
Keywords: Homocysteine levels; Ocular involvement; Retinal vasculitis.
© Association of Clinical Biochemists of India 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased serum level of homocysteine correlates with retinal nerve fiber layer thinning in diabetic retinopathy.Mol Vis. 2016 Dec 2;22:1352-1360. eCollection 2016. Mol Vis. 2016. PMID: 27994434 Free PMC article.
-
The relation between serum homocysteine level and eye involvement in Behçet's disease.Arch Iran Med. 2008 Nov;11(6):625-8. Arch Iran Med. 2008. PMID: 18976033
-
Serum homocysteine level is increased and correlated with endothelin-1 and nitric oxide in Behçet's disease.Br J Ophthalmol. 2002 Jun;86(6):653-7. doi: 10.1136/bjo.86.6.653. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002. PMID: 12034688 Free PMC article.
-
Homocysteine in ocular diseases.Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Oct 23;450:316-21. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.09.007. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 26343924 Review.
-
Serum/plasma homocysteine levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Jun;39(6):1725-1736. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-04985-w. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32090304
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources