Recent Advances in the Development of Non-PIKKs Targeting Small Molecule Inhibitors of DNA Double-Strand Break Repair
- PMID: 35463312
- PMCID: PMC9020266
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.850883
Recent Advances in the Development of Non-PIKKs Targeting Small Molecule Inhibitors of DNA Double-Strand Break Repair
Abstract
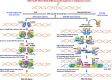
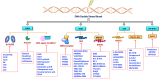
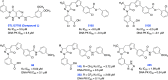
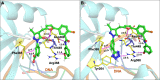
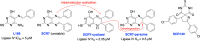
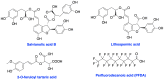
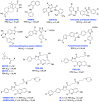
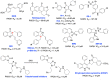
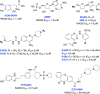
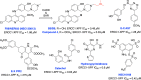
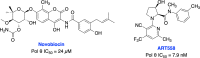
The vast majority of cancer patients receive DNA-damaging drugs or ionizing radiation (IR) during their course of treatment, yet the efficacy of these therapies is tempered by DNA repair and DNA damage response (DDR) pathways. Aberrations in DNA repair and the DDR are observed in many cancer subtypes and can promote de novo carcinogenesis, genomic instability, and ensuing resistance to current cancer therapy. Additionally, stalled or collapsed DNA replication forks present a unique challenge to the double-strand DNA break (DSB) repair system. Of the various inducible DNA lesions, DSBs are the most lethal and thus desirable in the setting of cancer treatment. In mammalian cells, DSBs are typically repaired by the error prone non-homologous end joining pathway (NHEJ) or the high-fidelity homology directed repair (HDR) pathway. Targeting DSB repair pathways using small molecular inhibitors offers a promising mechanism to synergize DNA-damaging drugs and IR while selective inhibition of the NHEJ pathway can induce synthetic lethality in HDR-deficient cancer subtypes. Selective inhibitors of the NHEJ pathway and alternative DSB-repair pathways may also see future use in precision genome editing to direct repair of resulting DSBs created by the HDR pathway. In this review, we highlight the recent advances in the development of inhibitors of the non-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinases (non-PIKKs) members of the NHEJ, HDR and minor backup SSA and alt-NHEJ DSB-repair pathways. The inhibitors described within this review target the non-PIKKs mediators of DSB repair including Ku70/80, Artemis, DNA Ligase IV, XRCC4, MRN complex, RPA, RAD51, RAD52, ERCC1-XPF, helicases, and DNA polymerase θ. While the DDR PIKKs remain intensely pursued as therapeutic targets, small molecule inhibition of non-PIKKs represents an emerging opportunity in drug discovery that offers considerable potential to impact cancer treatment.
Keywords: DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair; DNA repair and DNA damage response (DDR); homology directed repair (HDR); non-PIKKs inhibitors; non-homologous end joining (NHEJ); polymerase theta-mediated end joining (TMEJ); single-strand annealing (SSA); synthetic lethality.
Copyright © 2022 Kelm, Samarbakhsh, Pillai, VanderVere-Carozza, Aruri, Pandey, Pawelczak, Turchi and Gavande.
Conflict of interest statement
KSP is a Vice-President of Research and JJT is a cofounder and CSO of NERx Biosciences. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

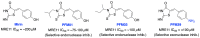
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of DNA double strand break repair and chromosome aberration formation.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;104(1-4):14-20. doi: 10.1159/000077461. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15162010 Review.
-
Reconstitution of Mycobacterium marinum Nonhomologous DNA End Joining Pathway in Leishmania.mSphere. 2022 Jun 29;7(3):e0015622. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00156-22. Epub 2022 Jun 13. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 35695492 Free PMC article.
-
New Facets of DNA Double Strand Break Repair: Radiation Dose as Key Determinant of HR versus c-NHEJ Engagement.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 6;24(19):14956. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914956. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative-NHEJ is a mechanistically distinct pathway of mammalian chromosome break repair.PLoS Genet. 2008 Jun 27;4(6):e1000110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000110. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18584027 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Strand Annealing Plays a Major Role in Double-Strand DNA Break Repair following CRISPR-Cas9 Cleavage in Leishmania.mSphere. 2019 Aug 21;4(4):e00408-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00408-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31434745 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
STL127705 synergize with olaparib in castration-resistant prostate cancer by inhibiting homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining repair.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 May 15;13(5):2030-2040. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37293174 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of Neural Stem Cells-Overexpressed Ku70 Improves Neurological Deficits in a Mice Model of Cerebral Ischemia Stroke.Neurochem Res. 2024 Mar;49(3):718-731. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04065-w. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38063947
-
Potential clinical treatment prospects behind the molecular mechanism of alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT).J Cancer. 2023 Jan 31;14(3):417-433. doi: 10.7150/jca.80097. eCollection 2023. J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36860927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Horizons of Synthetic Lethality in Cancer: Current Development and Future Perspectives.J Med Chem. 2024 Jul 25;67(14):11488-11521. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00113. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38955347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AZD-7648, a DNA-PK Inhibitor, Induces DNA Damage, Apoptosis, and Cell Cycle Arrest in Chronic and Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15331. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015331. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ray U, Raghavan SC. Inhibitors of DNA Double-Strand Break Repair at the Crossroads of Cancer Therapy and Genome Editing. Biochem Pharmacol (2020) 182:114195. - PubMed
-
- Chapman JR, Taylor MR, Boulton SJ. Playing the End Game: DNA Double Strand Break Repair Pathway Choice. Mol Cell (2012) 47:497–510. - PubMed
-
- O’Driscoll M, Jeggo PA. The Role of Double-Strand Break Repair-Insights From Human Genetics. Nat Rev Genet (2006) 7:45–54. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

