Development and External Validation of a Simple-To-Use Dynamic Nomogram for Predicting Breast Malignancy Based on Ultrasound Morphometric Features: A Retrospective Multicenter Study
- PMID: 35463357
- PMCID: PMC9021381
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.868164
Development and External Validation of a Simple-To-Use Dynamic Nomogram for Predicting Breast Malignancy Based on Ultrasound Morphometric Features: A Retrospective Multicenter Study
Abstract
Background: With advances in high-throughput computational mining techniques, various quantitative predictive models that are based on ultrasound have been developed. However, the lack of reproducibility and interpretability have hampered clinical use. In this study, we aimed at developing and validating an interpretable and simple-to-use US nomogram that is based on quantitative morphometric features for the prediction of breast malignancy.
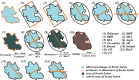
Methods: Successive 917 patients with histologically confirmed breast lesions were included in this retrospective multicentric study and assigned to one training cohort and two external validation cohorts. Morphometric features were extracted from grayscale US images. After feature selection and validation of regression assumptions, a dynamic nomogram with a web-based calculator was developed. The performance of the nomogram was assessed with respect to calibration, discrimination, and clinical usefulness.
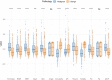
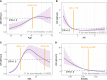
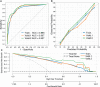
Results: Through feature selection, three morphometric features were identified as being the most optimal for predicting malignancy, and all regression assumptions of the prediction model were met. Combining all these predictors, the nomogram demonstrated a good discriminative performance in the training cohort and in the two external validation cohorts with AUCs of 0.885, 0.907, and 0.927, respectively. In addition, calibration and decision curves analyses showed good calibration and clinical usefulness.
Conclusions: By incorporating US morphometric features, we constructed an interpretable and easy-to-use dynamic nomogram for quantifying the probability of breast malignancy. The developed nomogram has good generalization abilities, which may fit into clinical practice and serve as a potential tool to guide personalized treatment. Our findings show that quantitative morphometric features from different ultrasound machines and systems can be used as imaging surrogate biomarkers for the development of robust and reproducible quantitative ultrasound dynamic models in breast cancer research.
Keywords: breast cancer; models; morphometrics; nomogram; quantitative imaging; ultrasound.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Zhang, Liu, Bao, Li and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Pan B, Yao R, Zhu QL, Wang CJ, You SS, Zhang J, et al. Clinicopathological Characteristics and Long-Term Prognosis of Screening Detected Non-Palpable Breast Cancer by Ultrasound in Hospital-Based Chinese Population (2001-2014). Oncotarget (2016) 7(47):76840–51. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12319 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

