Genome Structures and Evolution Analysis of Hsp90 Gene Family in Brassica napus Reveal the Possible Roles of Members in Response to Salt Stress and the Infection of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
- PMID: 35463405
- PMCID: PMC9022010
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.854034
Genome Structures and Evolution Analysis of Hsp90 Gene Family in Brassica napus Reveal the Possible Roles of Members in Response to Salt Stress and the Infection of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
Abstract
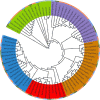
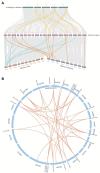
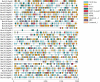
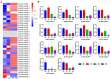
Heat shock proteins 90 (Hsp90s) are conserved proteins participating in the responses to heat stress and are found to be involved in different kinds of abiotic and biotic stresses. Brassica napus (B. napus) is an important heteropolyploid crop, producing edible oil. Salt stress is one of the most important hazards to the growth of rape in the world, while Sclerotinia stem rot is one of the most serious diseases, caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (S. sclerotiorum). In this study, the evolution of Hsp90 genes and their responses to these two stresses were elucidated. Bioinformatic analysis through the whole genome of B. napus identified 35 Hsp90 gene family members. Five groups were obtained via phylogenetic analysis with the 35 Hsp genes, Hsps from its two ancestor species Brassica rapa, Brassica oleracea, and AtHsps. Gene structure and conservative motif analysis of these 35 Hsps indicated that the Hsps were relatively conservative in each group. Strong collinearity was also detected between the genomes of Brassica rapa, Brassica oleracea and B. napus, along with identifying syntenic gene pairs of Hsps among the three genomes. In addition, whole genome duplication was discovered as the main reason for the generation of BnHsp gene family. The analysis of cis-acting elements indicated that BnHsp90 might be involved in a variety of abiotic and biotic stress responses. Analysis of the expression pattern indicated that BnHsp90 participates in the responses of B. napus to salt stress and the infection of S. sclerotiorum. Fourteen and nine BnHsp90s were validated to be involved in the defense responses of B. napus against salt stress and S. sclerotiorum, respectively. Our results provide new insights for the roles of BnHsp90s in the responses of B. napus to salt stress and S. sclerotiorum.
Keywords: Brassica napus; Hsp90; Sclerotinia sclerotiorum; heat shock protein; salt stress.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Liu, Ju, Xue, Wang, Wang and Hou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic breakthroughs in the Brassica napus-Sclerotinia sclerotiorum interactions.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Nov 23;14:1276055. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1276055. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38078117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of cupin_1 domain-containing members involved in the responses to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and abiotic stress in Brassica napus.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 1;13:983786. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.983786. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35979083 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of GYF-Domain Encoding Genes in Three Brassica Species and Their Expression Responding to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Brassica napus.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 15;14(1):224. doi: 10.3390/genes14010224. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672966 Free PMC article.
-
TMT-based quantitative proteomics analyses reveal novel defense mechanisms of Brassica napus against the devastating necrotrophic pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum.J Proteomics. 2016 Jun 30;143:265-277. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26947552
-
Sclerotinia Stem Rot Resistance in Rapeseed: Recent Progress and Future Prospects.J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Mar 17;69(10):2965-2978. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07351. Epub 2021 Mar 5. J Agric Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33667087 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the HSP90 Gene Family in Relation to Developmental and Abiotic Stress in Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe).Plants (Basel). 2025 May 29;14(11):1660. doi: 10.3390/plants14111660. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508332 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Survey of Heat Shock Proteins in Liriodendron chinense Provides Insight into Evolution, Characterization, and Functional Diversities.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 30;23(23):15051. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315051. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499378 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of hub genes associated with biotic and abiotic stresses by modular gene co-expression analysis in Oryza sativa L.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 12;15(1):8465. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92942-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40069264 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of HSP90 family gene in cotton and their potential role in salt stress tolerance.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jul 2;16:1574604. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1574604. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40672555 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic breakthroughs in the Brassica napus-Sclerotinia sclerotiorum interactions.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Nov 23;14:1276055. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1276055. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38078117 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

