Profiling Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Patterns in Human Aortic and Mitral Valves
- PMID: 35463757
- PMCID: PMC9019152
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.840647
Profiling Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Patterns in Human Aortic and Mitral Valves
Abstract
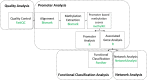
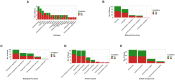
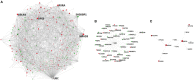
Cardiac valves exhibit highly complex structures and specialized functions that include dynamic interactions between cells, extracellular matrix (ECM) and their hemodynamic environment. Valvular gene expression is tightly regulated by a variety of mechanisms including epigenetic factors such as histone modifications, RNA-based mechanisms and DNA methylation. To date, methylation fingerprints of non-diseased human aortic and mitral valves have not been studied. In this work we analyzed the differential methylation profiles of 12 non-diseased aortic and mitral valve tissue samples (in matched pairs). Analysis of methylation data [reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS)] of 16,101 promoters genome-wide revealed 584 differentially methylated (DM) promoters, of which 13 were reported in endothelial mesenchymal trans-differentiation (EMT), 37 in aortic and mitral valve disease and 7 in ECM remodeling. Both functional classification as well as network analysis showed that the genes associated with the DM promoters were enriched for WNT-, Cadherin-, Endothelin-, PDGF-, HIF-1 and VEGF- signaling implicated in valvular physiology and pathophysiology. Additional enrichment was detected for TGFB-, NOTCH- and Integrin- signaling involved in EMT as well as ECM remodeling. This data provides the first insight into differential regulation of human aortic and mitral valve tissue and identifies candidate genes linked to DM promoters. Our work will improve the understanding of valve biology, valve tissue engineering approaches and contributes to the identification of relevant drug targets.
Keywords: HIF-1 signaling pathway; NOTCH signaling; endothelial mesenchymal trans-differentiation (EMT); epigenetics; extracellular matrix (ECM); heart valves; promoters; regulation of actin cytoskeleton.
Copyright © 2022 Halawa, Latif, Tseng, Ibrahim, Chester, Moustafa, Aguib and Yacoub.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Roy A, Brand NJ, Yacoub MH. Molecular characterization of interstitial cells isolated from human heart valves. J Heart Valve Dis. (2000) 9:459–464. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

