Determinants of Non-calcified Low-Attenuation Coronary Plaque Burden in Patients Without Known Coronary Artery Disease: A Coronary CT Angiography Study
- PMID: 35463764
- PMCID: PMC9021435
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.824470
Determinants of Non-calcified Low-Attenuation Coronary Plaque Burden in Patients Without Known Coronary Artery Disease: A Coronary CT Angiography Study
Abstract
Background: Although epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) is associated with coronary artery disease (CAD), it is unclear whether EAT volume (EAV) can be used to diagnose high-risk coronary plaque burden associated with coronary events. This study aimed to investigate (1) the prognostic impact of low-attenuation non-calcified coronary plaque (LAP) burden on patient level analysis, and (2) the association of EAV with LAP volume in patients without known CAD undergoing coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA).
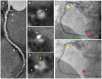
Materials and methods: This retrospective study consisted of 376 patients (male, 57%; mean age, 65.2 ± 13 years) without known CAD undergoing CCTA. Percent LAP volume (%LAP, <30 HU) was calculated as the LAP volume divided by the vessel volume. EAT was defined as adipose tissue with a CT attenuation value ranging from -250 to -30 HU within the pericardial sac. The primary endpoint was a composite event of death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and unstable angina and worsening symptoms requiring unplanned coronary revascularization >3 months after CCTA. The determinants of %LAP (Q4) were analyzed using a multivariable logistic regression model.
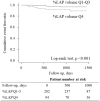
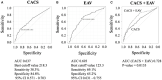
Results: During the follow-up period (mean, 2.2 ± 0.9 years), the primary endpoint was observed in 17 patients (4.5%). The independent predictors of the primary endpoint were %LAP (Q4) (hazard ratio [HR], 3.05; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09-8.54; p = 0.033] in the Cox proportional hazard model adjusted by CAD-RADS category. Cox proportional hazard ratio analysis demonstrated that %LAP (Q4) was a predictor of the primary endpoint, independnet of CAD severity, Suita score, EAV, or CACS. The independent determinants of %LAP (Q4) were CACS ≥218.3 (p < 0.0001) and EAV ≥125.3 ml (p < 0.0001). The addition of EAV to CACS significantly improved the area under the curve (AUC) to identify %LAP (Q4) than CACS alone (AUC, EAV + CACS vs. CACS alone: 0.728 vs. 0.637; p = 0.013).
Conclusions: CCTA-based assessment of EAV, CACS, and LAP could help improve personalized cardiac risk management by administering patient-suited therapy.
Keywords: chronic coronary syndrome (CCS); coronary CT angiography; coronary artery calcium score; epicardial adipose tissue; high-risk plaque; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Yamaura, Otsuka, Ishikawa, Shirasawa, Fukuda and Kasayuki.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Commentary: Plaque Features and Epicardial Fat Volume for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment-A Key Role With Cardiac Computed Tomography?Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 29;9:896321. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.896321. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35571220 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Shaw LJ, Berman DS, Maron DJ, Mancini GBJ, Hayes SW, Hartigan PM, et al. . Optimal medical therapy with or without percutaneous coronary intervention to reduce ischemic burden: results from the clinical outcomes utilizing revascularization and aggressive drug evaluation (COURAGE) trial nuclear substudy. Circulation. (2008) 117:1283–91. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.743963 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

