Artificial Intelligence Assisting the Early Detection of Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis From Chest X-Rays: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 35463963
- PMCID: PMC9023793
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.874475
Artificial Intelligence Assisting the Early Detection of Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis From Chest X-Rays: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
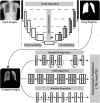
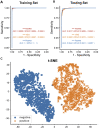
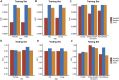
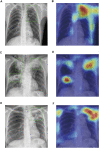
As a major infectious disease, tuberculosis (TB) still poses a threat to people's health in China. As a triage test for TB, reading chest radiography with traditional approach ends up with high inter-radiologist and intra-radiologist variability, moderate specificity and a waste of time and medical resources. Thus, this study established a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) based artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm, aiming at diagnosing TB on posteroanterior chest X-ray photographs in an effective and accurate way. Altogether, 5,000 patients with TB and 4,628 patients without TB were included in the study, totaling to 9,628 chest X-ray photographs analyzed. Splitting the radiographs into a training set (80.4%) and a testing set (19.6%), three different DCNN algorithms, including ResNet, VGG, and AlexNet, were trained to classify the chest radiographs as images of pulmonary TB or without TB. Both the diagnostic accuracy and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve were used to evaluate the performance of the three AI diagnosis models. Reaching an accuracy of 96.73% and marking the precise TB regions on the radiographs, ResNet algorithm-based AI outperformed the rest models and showed excellent diagnostic ability in different clinical subgroups in the stratification analysis. In summary, the ResNet algorithm-based AI diagnosis system provided accurate TB diagnosis, which could have broad prospects in clinical application for TB diagnosis, especially in poor regions with high TB incidence.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; chest radiograph; deep convolutional neural network; machine learning; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2022 Nijiati, Ma, Hu, Tuersun, Abulizi, Kelimu, Zhang, Li and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- He K., Zhang X., Ren S., Sun J. (2016). “Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition,” in Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, December 2016. 10.1109/cvpr.2016.90 - DOI
-
- Krizhevsky A., Sutskever I., Hinton G. (2012). ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 60, 84–90. NIPS. 10.1145/3065386 - DOI
-
- Organization W. H. (2016). Chest Radiography in Tuberculosis Detection: Summary of Current WHO Recommendations and Guidance on Programmatic Approaches. Geneva: World Health Organization.
-
- Organization W. H. (2021). WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis: Module 2: Screening: Systematic Screening for Tuberculosis Disease. Geneva: World Health Organization. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

