Effects of Different Ovulation Induction Regimens on Sex Hormone Levels and Serum CTRP3 and CTRP15 Levels in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- PMID: 35463985
- PMCID: PMC9019456
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6027878
Effects of Different Ovulation Induction Regimens on Sex Hormone Levels and Serum CTRP3 and CTRP15 Levels in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Different Ovulation Induction Regimens on Sex Hormone Levels and Serum CTRP3 and CTRP15 Levels in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).Biomed Res Int. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9891802. doi: 10.1155/2023/9891802. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 38075354 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: A retrospective cohort study aimed to explore the effects of different ovulation induction regimens on the levels of sex hormones and serum C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP3) and C1q/TNF-related protein-15 (CTRP15) in patients with PCOS.
Methods: A total of 100 patients with PCOS treated in the department of gynecology and obstetrics from February 2019 to April 2021 in our hospital were enrolled. The patients were arbitrarily assigned into control group and study group. The treatment effect, pregnancy rate, ovulation rate, follicle size, thickness of endometrium, number of mature follicles and ovulation, serum levels of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estradiol (E2), testosterone (T), serum CTRP3, CTRP15 and menstrual score were compared.
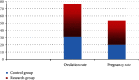
Results: There exhibited no statistical difference in baseline clinical data between the two kinds of patients. The therapeutic effects were compared, the effective rate was 98.00% in the study group, 13 cases in the control group, 20 cases in the effective group and 7 cases in the control group, and the effective rate was 86.00%. The effective rate in the study group was higher (P <0.05). The size of follicles and the thickness of endometrium in the two groups were compared before and after intervention. There exhibited no significant difference in the size of follicles and the thickness of endometrium before and after intervention (P >0.05). The size of follicles and the thickness of endometrium in the study group were significantly higher (P <0.05). The size of follicles and the thickness of endometrium in the study group were significantly higher (P <0.05). There exhibited no significant difference in the number of mature follicles and ovulation before and after intervention (P >0.05). After intervention, the number of mature follicles and ovulation in the two groups increased. The number of mature follicles and ovulation in the study group were (4.76 ± 0.90) and (4.48 ± 0.73), respectively, which were higher compared to the control group (2.45 ± 0.86) and (2.82 ± 0.84), respectively (P <0.05). The levels of serum LH, FSH, E2 and T were not significantly different before and after intervention. After the intervention of different ways of ovulation induction, the levels of serum LH, FSH, E2 and T in the two groups continued to decrease, and the levels of the above sex hormones in the study group were significantly lower (P <0.05). The menstrual score and the levels of serum CTRP3 and CTRP15 were compared before and after intervention. After intervention, the menstrual score of patients in both groups decreased, and the menstrual score of the study group was lower. In addition, the levels of serum CTRP3 and CTRP15 in the two groups decreased after intervention. Compared with the control group, the levels of CTRP3 and CTRP15 in the study group were lower after intervention (P <0.05). The ovulation rate and pregnancy rate of the two groups were compared. In the study group, there were 45 ovulation cases, the ovulation rate was 90.00% (45/50), the pregnancy rate was 33 cases, the pregnancy rate was 66.00% (33/50), and the ovulation rate in the control group was 31 cases, the ovulation rate was 62.00% (31/50), the pregnancy rate was 20 cases, and the pregnancy rate was 40.00% (20/50). The ovulation rate and pregnancy rate in the study group were higher (P <0.05).
Conclusion: Different ovulation induction regimens have different effects on the levels of sex hormones and serum CTRP3 and CTRP15 in patients with PCOS. Long-acting follicular phase regimens can effectively promote the therapeutic effect of patients and increase the ovulation rate and pregnancy rate. In addition, it can also reduce the levels of serum LH, follicle stimulating FSH, E2 and testosterone T, and help to promote the levels of serum CTRP3 and CTRP15, which is worth popularizing and applying in clinic.
Copyright © 2022 Maohua Ren et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dewailly D., Gronier H., Poncelet E., et al. Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): revisiting the threshold values of follicle count on ultrasound and of the serum AMH level for the definition of polycystic ovaries. Human Reproduction . 2011;26(11):3123–3129. doi: 10.1093/humrep/der297. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jingjun Z., Gao Y., Mengmeng T., Wang X. Effects of human chorionic gonadotropin injection day diameter 14mm follicle number ratio and follicular output rate on the pregnancy rate of fresh embryo transfer in patients with PCOS. Chinese Journal of Reproduction and contraception . 2020;40(12):986–993.
-
- Allegra C. J., Jessup J. M., Somerfield M. R., et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology Provisional Clinical Opinion: Testing forKRASGene Mutations in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Carcinoma to Predict Response to Anti–Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody Therapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology . 2009;27(12):2091–2096. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.21.9170. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous