A novel radiomics signature based on T2-weighted imaging accurately predicts hepatic inflammation in individuals with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a derivation and independent validation study
- PMID: 35464279
- PMCID: PMC9023815
- DOI: 10.21037/hbsn-21-23
A novel radiomics signature based on T2-weighted imaging accurately predicts hepatic inflammation in individuals with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a derivation and independent validation study
Abstract
Background: Currently, there are no effective methods for assessing hepatic inflammation without resorting to histological examination of liver tissue obtained by biopsy. T2-weighted images (T2WI) are routinely obtained from liver magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan sequences. We aimed to establish a radiomics signature based on T2WI (T2-RS) for assessment of hepatic inflammation in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Methods: A total of 203 individuals with biopsy-confirmed NAFLD from two independent Chinese cohorts with liver MRI examination were enrolled in this study. The hepatic inflammatory activity score (IAS) was calculated by the unweighted sum of the histologic scores for lobular inflammation and ballooning. One thousand and thirty-two radiomics features were extracted from the localized region of interest (ROI) in the right liver lobe of T2WI and, subsequently, selected by minimum redundancy maximum relevance and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) methods. The T2-RS was calculated by adding the selected features weighted by their coefficients.
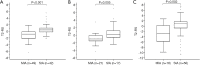
Results: Eighteen radiomics features from Laplacian of Gaussian, wavelet, and original images were selected for establishing T2-RS. The T2-RS value differed significantly between groups with increasing grades of hepatic inflammation (P<0.01). The T2-RS yielded an area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUROC) of 0.80 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.71-0.89] for predicting hepatic inflammation in the training cohort with excellent calibration. The AUROCs of T2-RS in the internal cohort and external validation cohorts were 0.77 (0.61-0.93) and 0.75 (0.63-0.84), respectively.
Conclusions: The T2-RS derived from radiomics analysis of T2WI shows promising utility for predicting hepatic inflammation in individuals with NAFLD.
Keywords: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD); inflammation activity; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); radiomics.
2022 Hepatobiliary Surgery and Nutrition. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://hbsn.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/hbsn-21-23/coif). MHZ serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Hepatobiliary Surgery and Nutrition. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Comment in
-
Hepatic inflammation: an important target for biomarker development in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2023 Jun 1;12(3):447-449. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-196. Epub 2023 May 18. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37351134 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Prediction of the Histopathological Grade of Soft Tissue Sarcomas: A Two-Center Study.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021 Jun;53(6):1683-1696. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27532. Epub 2021 Feb 18. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33604955
-
T2-Weighted Image-Based Radiomics Signature for Discriminating Between Seminomas and Nonseminoma.Front Oncol. 2019 Nov 28;9:1330. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01330. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31850216 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-based radiomics analysis to predict preoperative lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Gland Surg. 2020 Oct;9(5):1214-1226. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-479. Gland Surg. 2020. PMID: 33224796 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-Based Radiomics Models Developed With Features of the Whole Liver and Right Liver Lobe: Assessment of Hepatic Inflammatory Activity in Chronic Hepatic Disease.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Dec;52(6):1668-1678. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27197. Epub 2020 May 23. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32445618 Clinical Trial.
-
Elaboration of Multiparametric MRI-Based Radiomics Signature for the Preoperative Quantitative Identification of the Histological Grade in Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Aug;56(2):579-589. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28051. Epub 2022 Jan 18. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35040525
Cited by
-
Hepatic inflammation: an important target for biomarker development in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2023 Jun 1;12(3):447-449. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-196. Epub 2023 May 18. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37351134 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Novel Score Based on Controlled Attenuation Parameter Accurately Predicts Hepatic Steatosis in Individuals With Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Derivation and Independent Validation Study.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 1;15(3):e00680. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000680. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38240390 Free PMC article.
-
Reply to correspondence on "Hepatocellular carcinoma prediction model performance decreases with long-term antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients".Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):1044-1046. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0584. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39069724 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Efficient and Specific PDGFRβ-Targeting Dual-Mode T1-T2 MRI Nanoprobe for Early Diagnosis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jun;12(23):e2413788. doi: 10.1002/advs.202413788. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40051348 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive tests of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Chin Med J (Engl). 2022 Jan 27;135(5):532-546. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002027. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022. PMID: 35089884 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
