3D cell culture alters signal transduction and drug response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35464304
- PMCID: PMC9021830
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13297
3D cell culture alters signal transduction and drug response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
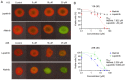
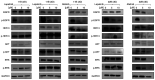
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) upregulation is a typical characteristic of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). However, tyrosine kinase inhibitors have not yet been able to achieve enough therapeutic benefit in clinical trials to justify their use in standard therapy regimens. At present, little is known about the reasons for this treatment failure. In the present study, the HNSCC cell lines UM-SCC-11B and UM-SCC-22B were tested for their response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) under 2D and 3D cell culture conditions. Absorption and luciferase-based viability assays were used for this, as well as optical evaluation via fluorescence microscopy. In addition, EGFR and HER3 expression as well as the downstream signalling pathways PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK were investigated using western blotting. Cell line UM-SCC-11B revealed a strong resistance to lapatinib under 3D cell culture conditions, while a good response to TKI therapy was observed under 2D cell culture conditions. An associated overexpression of phosphorylated HER3 under 3D cell culture conditions offered a plausible explanation for the altered treatment response. The results of the present study represent an idea of how signalling mechanisms of cancer cells can be changed using different cell culture methods. Overall, 3D cell culture could be an important component in the analysis of resistance mechanisms in cancer therapy.
Keywords: HER3 expression; afatinib; epidermal growth factor receptor; lapatinib; spheroid culture.
Copyright: © Heid et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of pharmacologic antagonists of epidermal growth factor receptor, PI3K and MEK signal kinases on NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation and IL-8 and VEGF expression in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines.Int J Cancer. 2002 Jun 1;99(4):538-48. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10398. Int J Cancer. 2002. PMID: 11992543
-
Coexpression of proangiogenic factors IL-8 and VEGF by human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma involves coactivation by MEK-MAPK and IKK-NF-kappaB signal pathways.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Feb;7(2):435-42. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11234901
-
Effects of culture method on response to EGFR therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 28;9(1):12480. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48764-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31462653 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: molecular bases for EGFR-targeted therapy.Pathol Res Pract. 2011 Jun 15;207(6):337-42. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2011.03.002. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2011. PMID: 21531084 Review.
-
Current challenges and clinical investigations of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)- and ErbB family-targeted agents in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 May;40(4):567-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 24216225 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging roles of 3D-culture systems in tackling tumor drug resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2023 Nov 21;6(4):788-804. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2023.93. eCollection 2023. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 38263982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative organ-on-a-chip platforms for exploring tumorigenesis and therapy in head and neck cancer.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 16;23(1):798. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06824-5. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40671128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes of immune microenvironment in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in 3D-4-culture compared to 2D-4-culture.J Transl Med. 2023 Oct 31;21(1):771. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04650-1. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37907991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, Winn DM, Austin DF, Greenberg RS, Preston-Martin S, Bernstein L, Schoenberg JB, Stemhagen A, Fraumeni JF., Jr Smoking and drinking in relation to oral and pharyngeal cancer. Cancer Res. 1988;48:3282–3287. - PubMed
-
- Grandis JR, Tweardy DJ. Elevated levels of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA are early markers of carcinogenesis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3579–3584. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
