Antimicrobial Peptides: Bringing Solution to the Rising Threats of Antimicrobial Resistance in Livestock
- PMID: 35464355
- PMCID: PMC9024325
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.851052
Antimicrobial Peptides: Bringing Solution to the Rising Threats of Antimicrobial Resistance in Livestock
Abstract
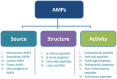
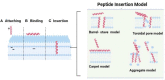
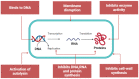
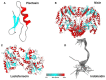
Antimicrobial therapy is the most applied method for treating and preventing bacterial infection in livestock. However, it becomes less effective due to the development of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Therefore, there is an urgent need to find new antimicrobials to reduce the rising rate of AMR. Recently, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have been receiving increasing attention due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, rapid killing activities, less toxicity, and cell selectivity. These features make them potent and potential alternative antimicrobials to be used in animals. Here, we discuss and summarize the AMPs in animals, classification, structures, mechanisms of action, and their potential use as novel therapeutic alternative antimicrobials to tackle the growing AMR threat.
Keywords: alternative antimicrobial; antimicrobial peptides (AMPs); antimicrobial resistance (AMR); bacterial infection; livestock.
Copyright © 2022 Saeed, Mergani, Aklilu and Kamaruzzman.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial Peptides and Cell-Penetrating Peptides: Non-Antibiotic Membrane-Targeting Strategies Against Bacterial Infections.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Feb 28;16:1203-1219. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S396566. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 36879855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial peptides used as growth promoters in livestock production.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Oct;105(19):7115-7121. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11540-3. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34499200 Review.
-
Synergism between Host Defence Peptides and Antibiotics Against Bacterial Infections.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(14):1238-1263. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200303122626. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32124698 Review.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy in Tackling Antimicrobial Resistance.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(38):4303-4314. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170815102441. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28814242 Review.
-
Fijian Farmers' Attitude and Knowledge Towards Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance in Livestock Production Systems-A Qualitative Study.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 30;9:838457. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.838457. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35433900 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial activity and mechanistic insights of AMP-17 against drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its efficacy in wound infection management.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Aug 8;15:1634825. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1634825. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40861483 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Protease Inhibitors as Emerging Antimicrobial Peptide Agents: A Comprehensive Review.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 24;16(5):582. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050582. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38794245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane Activity of Melittin and Magainin-I at Low Peptide-to-Lipid Ratio: Different Types of Pores and Translocation Mechanisms.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 4;14(9):1118. doi: 10.3390/biom14091118. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334885 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the classification, optimization, activity, and application of antimicrobial peptides.Front Microbiol. 2025 Apr 23;16:1582863. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1582863. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40336834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
University student perspectives on antimicrobial peptide use in farm animals.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 5;19(12):e0309986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309986. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39636793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Serwecińska L. Antimicrobials and antibiotic-resistant bacteria: A risk to the environment and to public health. Water (Switzerland). (2020) 12:3313. 10.3390/w12123313 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

