Comparative Analysis of the Fecal Microbiota of Relict Gull (Larus relictus) in Mu Us Desert (Hao Tongcha Nur) and Bojiang Haizi in Inner Mongolia, China
- PMID: 35464369
- PMCID: PMC9018992
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.860540
Comparative Analysis of the Fecal Microbiota of Relict Gull (Larus relictus) in Mu Us Desert (Hao Tongcha Nur) and Bojiang Haizi in Inner Mongolia, China
Abstract
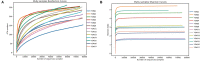
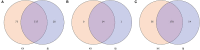
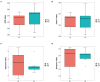
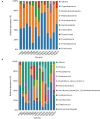
The gut microbiota contributes to host health by improving digestive efficiency and maintaining homeostasis. The relict gull (Larus relictus), a national first-class protected bird in China, is listed as vulnerable in the International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List. Here, 16S rRNA gene sequencing was performed to characterize and compare the community composition and diversity of the gut microbiota sampled from relict gulls in two breeding sites. In total, 418 operational taxonomic units (OUTs) were obtained and classified into 15 phyla and 228 genera. Alpha diversity analysis revealed no significant differences in community diversity among the two breeding sites. Beta diversity analyses showed that the microbial communities at the two sites were different. Six dominant phyla and fourteen dominant genera were identified. The most abundant bacterial genera had a significant relationship with the diet and living environment, and some bacterial genera were found to adapt to the plateau environment in which relict gulls live, which enables the relict gulls to use local resources effectively to accumulate energy. Simultaneously, a variety of highly abundant pathogenic bacteria were found, suggesting that these gulls may spread diseases among the local gull population. Certain measures should be taken to protect this species and to prevent the spread of diseases.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene; Bojiang Haizi; Mu Us Desert; gut microbiota; high-throughput sequencing; relict gulls.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Du, Liu and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of the gut bacteria of the relict gull (Larus Relictus) and black-necked grebe (Podiceps Nigricollis) in Erdos Relic Gull National Nature Reserve in Inner Mongolia, China.PeerJ. 2023 Jul 10;11:e15462. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15462. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37456862 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Gut Bacteria of Four Waterbirds Species in Taolimiao-Alashan Nur (T-A Nur) in Erdos Relic Gull National Nature Reserve, Inner Mongolia, China.Ecol Evol. 2025 May 13;15(5):e71432. doi: 10.1002/ece3.71432. eCollection 2025 May. Ecol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40370353 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Fecal Bacterial Microbiota of Six Bird Species.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Dec 8;8:791287. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.791287. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34957285 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal dispersal and longitudinal migration in the Relict Gull Larus relictus across the Inner-Mongolian Plateau.PeerJ. 2017 May 25;5:e3380. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3380. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 28560115 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic and Antibiotic Resistance Analysis of the Gut Microbiota in Larus relictus and Anatidae Species Inhabiting the Honghaizi Wetland of Ordos, Inner Mongolia, from 2021 to 2023.Microorganisms. 2024 May 13;12(5):978. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12050978. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792807 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Whole-genome resequencing landscape of adaptive evolution in Relict gull (Larus relictus).BMC Genomics. 2025 Jan 24;26(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11257-x. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39856550 Free PMC article.
-
Significant Differences in Intestinal Bacterial Communities of Sympatric Bean Goose, Hooded Crane, and Domestic Goose.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jun 5;14(11):1688. doi: 10.3390/ani14111688. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891737 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of fecal microbiota of central and eastern black-necked cranes (Grus nigricollis) wintering in Yunnan Province, China.PeerJ. 2025 May 27;13:e19520. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19520. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40452926 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of the gut bacteria of the relict gull (Larus Relictus) and black-necked grebe (Podiceps Nigricollis) in Erdos Relic Gull National Nature Reserve in Inner Mongolia, China.PeerJ. 2023 Jul 10;11:e15462. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15462. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37456862 Free PMC article.
-
Similarities and differences: species and diet impact gut microbiota of captive pheasants.PeerJ. 2024 Mar 26;12:e16979. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16979. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38560462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He F, Melville D, Xing X, Ren Y. A review on studies of the Relict Gull Larus relictus. Chin J Zool. (2002) 37:65–70 (in Chinese: ). 10.13859/j.cjz.2002.03.019 - DOI
-
- BirdLife International . Species factsheet: Larus relictus [OL] (2020). Available online at: http://www.brdlife.org.
-
- Xiao H, Wang Q, Wang Z, Hu C, Cai Q. Analysis on diversity and composition of waterbirds from Hongjiannao wetland, Shaanxi Province. Sichuan J Zool. (2010). 29:605–8 (in Chinese: ). Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=SCDW201005027&DbNa...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

