Advances in the Immune Regulatory Role of Non-Coding RNAs (miRNAs and lncRNAs) in Insect-Pathogen Interactions
- PMID: 35464405
- PMCID: PMC9020863
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.856457
Advances in the Immune Regulatory Role of Non-Coding RNAs (miRNAs and lncRNAs) in Insect-Pathogen Interactions
Abstract
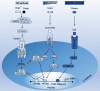
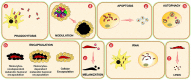
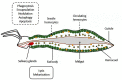
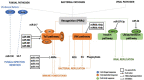
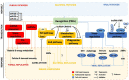
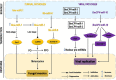
Insects are by far the most abundant and diverse living organisms on earth and are frequently prone to microbial attacks. In other to counteract and overcome microbial invasions, insects have in an evolutionary way conserved and developed immune defense mechanisms such as Toll, immune deficiency (Imd), and JAK/STAT signaling pathways leading to the expression of antimicrobial peptides. These pathways have accessory immune effector mechanisms, such as phagocytosis, encapsulation, melanization, nodulation, RNA interference (RNAi), lysis, autophagy, and apoptosis. However, pathogens evolved strategies that circumvent host immune response following infections, which may have helped insects further sophisticate their immune response mechanisms. The involvement of ncRNAs in insect immunity is undeniable, and several excellent studies or reviews have investigated and described their roles in various insects. However, the functional analyses of ncRNAs in insects upon pathogen attacks are not exhaustive as novel ncRNAs are being increasingly discovered in those organisms. This article gives an overview of the main insect signaling pathways and effector mechanisms activated by pathogen invaders and summarizes the latest findings of the immune modulation role of both insect- and pathogen-encoded ncRNAs, especially miRNAs and lncRNAs during insect-pathogen crosstalk.
Keywords: immune modulation; insect immune pathways; insect–pathogen interaction; mRNA targets; miRNAs and lncRNAs.
Copyright © 2022 Moure, Tan, Sha, Lu, Shao, Yang, Wang and Cui.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insect-pathogen crosstalk and the cellular-molecular mechanisms of insect immunity: uncovering the underlying signaling pathways and immune regulatory function of non-coding RNAs.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 24;14:1169152. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1169152. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37691928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Characterization of Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) Differentially Expressed During Insect Development.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2360:1-8. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1633-8_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34495502
-
Insect immunology and hematopoiesis.Dev Comp Immunol. 2016 May;58:102-18. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2015.12.006. Epub 2015 Dec 13. Dev Comp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26695127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Progress in innate immunity-related genes in insects].Yi Chuan. 2018 Jun 20;40(6):451-466. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-363. Yi Chuan. 2018. PMID: 29959118 Review. Chinese.
-
The Potential Biological Roles of Circular RNAs in the Immune Systems of Insects to Pathogen Invasion.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 12;14(4):895. doi: 10.3390/genes14040895. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107653 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of insect gut microbiota in host fitness, detoxification and nutrient supplementation.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024 Apr 26;117(1):71. doi: 10.1007/s10482-024-01970-0. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024. PMID: 38668783 Review.
-
The Aedes aegypti siRNA pathway mediates broad-spectrum defense against human pathogenic viruses and modulates antibacterial and antifungal defenses.PLoS Biol. 2022 Jun 9;20(6):e3001668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001668. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 35679279 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin1 inhibits Nosema bombycis proliferation by promoting Domeless- and Hop-mediated JAK-STAT pathway activation in Bombyx mori.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0367123. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03671-23. Epub 2024 May 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38690912 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological Roles of TmToll-2 in Response to Escherichia coli Systemic Infection in Tenebrio molitor.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 21;23(22):14490. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214490. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430968 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Long Non-Coding RNA-Mediated Regulatory Networks of Plutella xylostella in Response to Metarhizium anisopliae Infection.Insects. 2022 Oct 9;13(10):916. doi: 10.3390/insects13100916. Insects. 2022. PMID: 36292864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lundgren JG, Jurat-Fuentes JL. The Physiology and Ecology of Host Defense Against Microbial Invaders. Insect Pathol (2012) 2nd edition):460–80. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-384984-7.00013-0 - DOI
-
- Siva-Jothy MT, Moret Y, Rolff J. Insect Immunity: An Evolutionary Ecology Perspective. In: Simpson SJ, editor. Advances in Insect Physiology, vol. 32 . Academic Press; (2005). p. 1–48.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

