What Is IL-1 for? The Functions of Interleukin-1 Across Evolution
- PMID: 35464444
- PMCID: PMC9020223
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.872155
What Is IL-1 for? The Functions of Interleukin-1 Across Evolution
Abstract
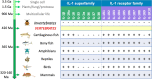
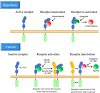
Interleukin-1 is a cytokine with potent inflammatory and immune-amplifying effects, mainly produced by macrophages during defensive reactions. In mammals, IL-1 is a superfamily of eleven structurally similar proteins, all involved in inflammation or its control, which mainly act through binding to specific receptors on the plasma membrane of target cells. IL-1 receptors are also a family of ten structurally similar transmembrane proteins that assemble in heterocomplexes. In addition to their innate immune/inflammatory effects, the physiological role of IL-1 family cytokines seems to be linked to the development of adaptive immunity in vertebrates. We will discuss why IL-1 developed in vertebrates and what is its physiological role, as a basis for understanding when and how it can be involved in the initiation and establishment of pathologies.
Keywords: adaptive immunity; evolution; inflammation; innate immunity; interleukin-1.
Copyright © 2022 Boraschi.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the study was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

