The Inhibition of CD40/CD154 Costimulatory Signaling in the Prevention of Renal Transplant Rejection in Nonhuman Primates: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis
- PMID: 35464470
- PMCID: PMC9022482
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.861471
The Inhibition of CD40/CD154 Costimulatory Signaling in the Prevention of Renal Transplant Rejection in Nonhuman Primates: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis
Abstract
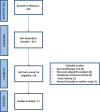
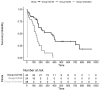
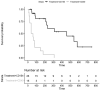
The prevention of allograft transplant rejection by inhibition of the CD40/CD40L costimulatory pathway has been described in several species. We searched pubmed for studies reporting the prevention of kidney transplant rejection in nonhuman primates utilizing either anti CD40 or anti CD40L (CD154) treatment. Inclusion of data required treatment with anti CD40 or anti CD154 as monotherapy treatment arms, full text available, studies conducted in nonhuman primate species, the transplant was renal transplantation, sufficient duration of treatment to assess long term rejection, and the reporting of individual graft survival or survival duration. Eleven publications were included in the study. Rejection free survival was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier (KM) life test methods to estimate the survival functions. The 95% CI for the medians was also calculated. A log-rank test was used to test the equality of the survival curves between control and treatment arms (CD40 and CD154). The hazard ratio for CD154 compared to CD40 and 95% CI was calculated using a Cox proportional-hazards model including treatment as the covariate to assess the magnitude of the treatment effect. Both anti CD40 and anti CD154 treatments prevented acute and long term graft rejection. The median (95% CI) rejection free survival was 131 days (84,169 days) in the anti CD40 treated animals and 352 days (173,710 days) in the anti CD154 treated animals. Median survival in the untreated animals was 6 days. The inhibition of transplant rejection was more durable in the anti CD154 group compared to the anti CD40 group after cessation of treatment. The median (95% CI) rejection free survival after cessation of treatment was 60 days (21,80 days) in the anti CD40 treated animals and 230 days (84,552 days) in the anti CD154 treated animals.
Keywords: CD154; CD40; CD40L; renal transplant; tolerance; transplant rejection.
Copyright © 2022 Perrin and Magill.
Conflict of interest statement
SP declares that he is employed by Eledon Pharmaceuticals. Eledon is developing an anti CD40L antibody for renal and islet cell transplant. MM is an independent paid statistical consultant to Eledon Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fc-Silent Anti-CD154 Domain Antibody Effectively Prevents Nonhuman Primate Renal Allograft Rejection.Am J Transplant. 2017 May;17(5):1182-1192. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14197. Epub 2017 Feb 25. Am J Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28097811 Free PMC article.
-
CD40 expression on graft infiltrates and parenchymal CD154 (CD40L) induction in human chronic renal allograft rejection.Kidney Int. 1999 Apr;55(4):1543-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00379.x. Kidney Int. 1999. PMID: 10201021
-
Blockade of CD40-CD154 at the time of donor-specific blood transfusion does not lead to prolonged kidney allograft survival in nonhuman primates.Transplantation. 2002 Mar 27;73(6):862-6. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200203270-00006. Transplantation. 2002. PMID: 11923684
-
CD40-CD40L Blockade: Update on Novel Investigational Therapeutics for Transplantation.Transplantation. 2023 Jul 1;107(7):1472-1481. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004469. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Transplantation. 2023. PMID: 36584382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CD154-CD40 costimulatory pathway in transplantation.Transplantation. 2002 Jan 15;73(1 Suppl):S36-9. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200201151-00012. Transplantation. 2002. PMID: 11810060 Review.
Cited by
-
Adoptive transfer of allergen-expressing B cells prevents IgE-mediated allergy.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 23;14:1286638. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1286638. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38077381 Free PMC article.
-
Differential induction of donor-reactive Foxp3+ regulatory T cell via blockade of CD154 vs CD40.Am J Transplant. 2024 Aug;24(8):1369-1381. doi: 10.1016/j.ajt.2024.03.033. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Am J Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38552961 Free PMC article.
-
Xenotransplantation: How close are we to clinical applications?Life Med. 2024 Oct 3;3(5):lnae037. doi: 10.1093/lifemedi/lnae037. eCollection 2024 Oct. Life Med. 2024. PMID: 39872441 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Local delivery of an adenosine receptor agonist reduces inflammation associated with contact hypersensitivity.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Mar 8. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01831-x. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40057627
-
Contributions of Europeans to Xenotransplantation Research: 2. Pig Islet and Cell Xenotransplantation.Transpl Int. 2025 Apr 17;38:14143. doi: 10.3389/ti.2025.14143. eCollection 2025. Transpl Int. 2025. PMID: 40313362 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Freeman GJ, Freedman AS, Segil JM, Lee G, Whitman JF, Nadler LM. B7, A New Member of the Ig Superfamily With Unique Expression on Activated and Neoplastic B Cells. J Immunol (1989) 143(8):2714–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

