The Prognostic Value of Natural Killer Cells and Their Receptors/Ligands in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35464489
- PMCID: PMC9021421
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.872353
The Prognostic Value of Natural Killer Cells and Their Receptors/Ligands in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Natural killer (NK) cells play major roles in eliminating tumor cells. Preliminary studies have shown that NK cells and their receptors/ligands have prognostic value in malignant tumors. However, the relevance of NK cells and their receptors/ligands level to the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear.
Methods: Several electronic databases were searched from database inception to November 8, 2021. Random effects were introduced to this meta-analysis. The relevance of NK cells and their receptors/ligands level to the prognosis of HCC was evaluated using hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence interval (95%CI).
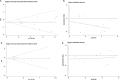
Results: 26 studies were included in the analysis. The pooled results showed that high NK cells levels were associated with better overall survival (HR=0.70, 95%CI 0.57-0.86, P=0.001) and disease-free survival (HR=0.61, 95%CI 0.40-0.93, P=0.022) of HCC patients. In subgroup analysis for overall survival, CD57+ NK cells (HR=0.70, 95%CI 0.55-0.89, P=0.004) had better prognostic value over CD56+ NK cells (HR=0.69, 95%CI 0.38-1.25, P=0.224), and intratumor NK cells had better prognostic value (HR=0.71, 95%CI 0.55-0.90, P=0.005) over peripheral NK cells (HR=0.66, 95%CI 0.41-1.06, P=0.088). In addition, high level of NK cell inhibitory receptors predicted increased recurrence of HCC, while the prognostic role of NK cell activating receptors remained unclear.
Conclusion: NK cells and their inhibitory receptors have prognostic value for HCC. The prognostic role of NK cell activating receptors is unclear and more high-quality prospective studies are essential to evaluate the prognostic value of NK cells and their receptors/ligands for HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; ligand; natural killer cells; prognosis; receptor.
Copyright © 2022 Xue, Ding, Meng, Yan, Liu, Li, Yao, Tian, Dong, Chen, Hong, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

