Software Analysis of Colonoscopy Videos Enhances Teaching and Quality Metrics
- PMID: 35464512
- PMCID: PMC9001872
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.23039
Software Analysis of Colonoscopy Videos Enhances Teaching and Quality Metrics
Abstract
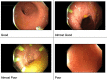
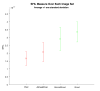
Purpose Machine learning algorithms were hypothesized as being able to predict the quality of colonoscopy luminal images. This is to enhance training and quality indicators in endoscopy. Methods A separate study involving a randomized controlled trial of capped vs. un-capped colonoscopies provided the colonoscopy videos for this study. Videos were analyzed with an algorithm devised by the Australian Institute for Machine Learning. The image analysis validated focus measure, steerable filters-based metrics (SFIL), was used to assess luminal visualization quality and was compared with two independent clinician assessments (C1 and C2). Goodman and Kruskal's gamma (G) measure was used to assess rank correlation data using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY). Results A total of 500 random colonoscopy video clips were extracted and analyzed, 88 being excluded. SFIL scores matched with C1 in 45% and C2 in 42% of cases, respectively. There was a significant correlation between SFIL and C1 (G = 0.644, p < 0.005) and SFIL and C2 (G = 0.734, p < 0.005). Conclusion This study demonstrates that machine learning algorithms can recognize the quality of luminal visualization during colonoscopy. We intend to apply this in the future to enhance colonoscopy training and as a metric for quality assessment.
Keywords: australia; cohort studies; colonoscopy; pilot project; software.
Copyright © 2022, Rajan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Institute of Medicine. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2000. To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System. - PubMed
-
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Healthcare. Colonoscopy Clinical Care Standard (revised 2020) [ Jan; 2022 ];https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/publications-and-resources/resource-... Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Healthcare. 2020
-
- Endocuff Vision-assisted colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial. Jacob A, Schafer A, Yong J, et al. ANZ J Surg. 2019;89:0–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous