Acute Severe Hypovolemic Hyponatremia in a Patient on Intravenous Dexamethasone
- PMID: 35464593
- PMCID: PMC9001806
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.23080
Acute Severe Hypovolemic Hyponatremia in a Patient on Intravenous Dexamethasone
Abstract
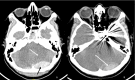
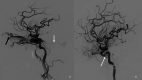
Hyponatremia is a commonly encountered electrolyte imbalance with varied etiology. Hyponatremia can be broadly classified as hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic hyponatremia based on the tonicity of plasma. Hypotonic hypovolemia is further classified as hypovolemic, euvolemic, and hypervolemic hyponatremia based on the volume status. Gastrointestinal fluid and electrolyte losses, secondary to vomiting and diarrhea, is an important predisposition to hypotonic hypovolemic hyponatremia. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) play a pivotal role in maintaining intravascular volume and serum sodium concentration. Dexamethasone is a potent glucocorticoid with minimal mineralocorticoid activity. It negatively affects the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, particularly with prolonged administration. In the index case, acute severe hypovolemic hyponatremia ensued on the third post-procedure (endovascular embolization of traumatic carotico-cavernous fistula (CCF)) day while the patient was on intravenous dexamethasone. This case underscores that even small fluid and electrolyte imbalance in the setting of dexamethasone therapy may lead to severe hypovolemic hyponatremia, which requires specific therapy.
Keywords: accidental head trauma; acute hyponatremia; carotico-cavernous fistula; dexamethasone; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Copyright © 2022, Peer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of hyponatremia: expert panel recommendations. Verbalis JG, Goldsmith SR, Greenberg A, Korzelius C, Schrier RW, Sterns RH, Thompson CJ. Am J Med. 2013;126:0–42. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
