Evaluation of an automated template-based treatment planning system for radiotherapy of anal, rectal and prostate cancer
- PMID: 35464888
- PMCID: PMC9020095
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2022.04.001
Evaluation of an automated template-based treatment planning system for radiotherapy of anal, rectal and prostate cancer
Abstract
Background and purpose: The Ethos system has enabled online adaptive radiotherapy (oART) by implementing an automated treatment planning system (aTPS) for both intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric modulated arc radiotherapy (VMAT) plan creation. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the quality of aTPS plans in the pelvic region.
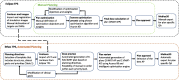
Material and methods: Sixty patients with anal (n = 20), rectal (n = 20) or prostate (n = 20) cancer were retrospectively re-planned with the aTPS. Three IMRT (7-, 9- and 12-field) and two VMAT (2 and 3 arc) automatically generated plans (APs) were created per patient. The duration of the automated plan generation was registered. The best IMRT-AP and VMAT-AP for each patient were selected based on target coverage and dose to organs at risk (OARs). The AP quality was analyzed and compared to corresponding clinically accepted and manually generated VMAT plans (MPs) using several clinically relevant dose metrics. Calculation-based pre-treatment plan quality assurance (QA) was performed for all plans.
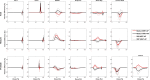
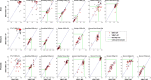
Results: The median total duration to generate the five APs with the aTPS was 55 min, 39 min and 35 min for anal, prostate and rectal plans, respectively. The target coverage and the OAR sparing were equivalent for IMRT-APs and VMAT-MPs, while VMAT-Aps.demonstrated lower target dose homogeneity and higher dose to some OARs. Both conformity and homogeneity index were equivalent (rectal) or better (anal and prostate) for IMRT-APs compared to VMAT-MPs. All plans passed the patient-specific QA tolerance limit.
Conclusions: The aTPS generates plans comparable to MPs within a short time-frame which is highly relevant for oART treatments.
Keywords: AP, automatically generated plan; Automated treatment planning; CN, conformity number; CT, computed tomography; CTV, clinical target volume; DVH, dose volume histogram; FFF, flattening filter free; GTV, gross tumor volume; HI, homogeneity index; IMRT, intensity modulated radiotherapy; Intelligent optimization engine; KPB, knowledge-based planning; Linac, Linear accelerators; MCO, multi-criteria optimization; MLC, multileaf collimator; MP, manually-generated plan; MR, magnetic resonance; MU, Monitor Unit; OAR, Organ at risk; Online adaptive radiotherapy; PTV, planning target volume; Pelvic cancer; Plan quality; QA, Quality assurance; SD, standard deviation; Template-based Ethos TPS; VMAT, volumetric arc radiotherapy; aTPS, automated treatment planning system; oART, online adaptive radiotherapy.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dosimetric comparison of MR-linac-based IMRT and conventional VMAT treatment plans for prostate cancer.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Jul 21;16(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01858-7. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34289868 Free PMC article.
-
Volumetric-modulated arc therapy for the treatment of a large planning target volume in thoracic esophageal cancer.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2013 May 6;14(3):4269. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v14i3.4269. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23652258 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy for the treatment of pituitary adenomas: A dosimetric comparison of three planning techniques.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020 Jul-Aug;25(4):586-593. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2020.04.020. Epub 2020 May 19. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020. PMID: 32508534 Free PMC article.
-
Robust optimization in lung treatment plans accounting for geometric uncertainty.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018 May;19(3):19-26. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12291. Epub 2018 Mar 10. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29524301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence applications in intensity modulated radiation treatment planning: an overview.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021 Dec;11(12):4859-4880. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-208. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021. PMID: 34888195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ROAR-A: re-optimization based Online Adaptive Radiotherapy of anal cancer, a prospective phase II trial protocol.BMC Cancer. 2024 Mar 25;24(1):374. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12111-1. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38528456 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing volumetric modulated arc therapy prostate planning using an automated Fine-Tuning process through dynamic adjustment of optimization parameters.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024 Aug 3;31:100619. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2024.100619. eCollection 2024 Jul. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39220116 Free PMC article.
-
In silico trial of simulation-free hippocampal-avoidance whole brain adaptive radiotherapy.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2023 Sep 9;28:100491. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2023.100491. eCollection 2023 Oct. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37772278 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Ethos intelligent optimization engine for left locally advanced breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 1;14:1399978. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1399978. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39015493 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the feasibility of using Ethos generated treatment plans for head and neck cancer patients.Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2023 Jun 27;27:100216. doi: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2023.100216. eCollection 2023 Sep. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37744525 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

