The Potential of Gut Microbiota Metabolic Capability to Detect Drug Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- PMID: 35464950
- PMCID: PMC9024311
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.839015
The Potential of Gut Microbiota Metabolic Capability to Detect Drug Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Abstract
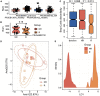
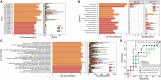
Gut microbiota plays an essential role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and affects drug responses. However, the underlying mechanism remains elusive and urgent to elucidate to explore the pathology and clinical treatment of RA. Therefore, we selected methotrexate (MTX) as an example of RA drugs to explore the interactions between the gut microbiota and drug responses and obtain an in-depth understanding of their correlation from the perspective of the metabolic capability of gut microbiota on drug metabolism. We identified 2,654 proteins and the corresponding genes involved in MTX metabolism and then profiled their abundances in the gut microbiome datasets of four cohorts. We found that the gut microbiota harbored various genes involved in MTX metabolism in healthy individuals and RA patients. Interestingly, the number of genes involved in MTX metabolism was not significantly different between response (R) and non-response (NR) groups to MTX, but the gene composition in the microbial communities significantly differed between these two groups. Particularly, several models were built based on clinical information, as well as data on the gene, taxonomical, and functional biomarkers by using the random forest algorithm and then validated. Our findings provide bases for clinical management not only of RA but also other gut microbiome-related diseases. First, it suggests that the potential metabolic capability of gut microbiota on drug metabolism is important because they affect drug efficiency; as such, clinical treatment strategies should incorporate the gene compositions of gut microbial communities, in particular genes involved in drug metabolism. Second, a suitable model can be developed to determine hosts' responses to drugs before clinical treatment.
Keywords: clinical medication; drug metabolism; gut microbiota; methotrexate; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Han, Zhang, Mao, Huang, Ren, Peng, Bai, Chen, Liu, Wang, Huang and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

