Red Nucleus Interleukin-6 Evokes Tactile Allodynia in Male Rats Through Modulating Spinal Pro-inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines
- PMID: 35465093
- PMCID: PMC9026175
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.820664
Red Nucleus Interleukin-6 Evokes Tactile Allodynia in Male Rats Through Modulating Spinal Pro-inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines
Abstract
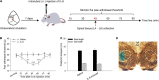
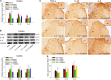
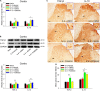
Our previous studies have clarified that red nucleus (RN) interleukin (IL)-6 is involved in the maintenance of neuropathic pain and produces a facilitatory effect by activating JAK2/STAT3 and ERK pathways. In this study, we further explored the immune molecular mechanisms of rubral IL-6-mediated descending facilitation at the spinal cord level. IL-6-evoked tactile allodynia was established by injecting recombinant IL-6 into the unilateral RN of naive male rats. Following intrarubral administration of IL-6, obvious tactile allodynia was evoked in the contralateral hindpaw of rats. Meanwhile, the expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-1β, and IL-6 were elevated in the contralateral spinal dorsal horn (L4-L6), blocking spinal TNF-α, IL-1β, or IL-6 with neutralizing antibodies relieved IL-6-evoked tactile allodynia. Conversely, the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and IL-10 were reduced in the contralateral spinal dorsal horn (L4-L6), an intrathecal supplement of exogenous TGF-β, or IL-10 attenuated IL-6-evoked tactile allodynia. Further studies demonstrated that intrarubral pretreatment with JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor AG490 suppressed the elevations of spinal TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 and promoted the expressions of TGF-β and IL-10 in IL-6-evoked tactile allodynia rats. However, intrarubral pretreatment with ERK inhibitor PD98059 only restrained the increase in spinal TNF-α and enhanced the expression of spinal IL-10. These findings imply that rubral IL-6 plays descending facilitation and produces algesic effect through upregulating the expressions of spinal pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 and downregulating the expressions of spinal anti-inflammatory cytokines TGF-β and IL-10 by activating JAK2/STAT3 and/or ERK pathways, which provides potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of pathological pain.
Keywords: allodynia; interleukin-10; interleukin-1β; interleukin-6; red nucleus; spinal cord; transforming growth factor-β; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Li, Xia, Tian, Feng, Yang, Xu, Guo, Li, Wang and Zeng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Red nucleus IL-6 mediates the maintenance of neuropathic pain by inducing the productions of TNF-α and IL-1β through the JAK2/STAT3 and ERK signaling pathways.Neuropathology. 2020 Aug;40(4):347-357. doi: 10.1111/neup.12653. Epub 2020 May 7. Neuropathology. 2020. PMID: 32380573
-
Red nucleus interleukin-1β evokes tactile allodynia through activation of JAK/STAT3 and JNK signaling pathways.J Neurosci Res. 2018 Dec;96(12):1847-1861. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24324. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Neurosci Res. 2018. PMID: 30216497
-
Red nucleus IL-33 facilitates the early development of mononeuropathic pain in male rats by inducing TNF-α through activating ERK, p38 MAPK, and JAK2/STAT3.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Jul 5;18(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02198-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34225736 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Progresses and Prospects of IL-37 in Central Nervous System Diseases.Brain Sci. 2022 May 31;12(6):723. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12060723. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35741608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Manual therapy and exercise effects on inflammatory cytokines: a narrative overview.Front Rehabil Sci. 2024 Apr 30;5:1305925. doi: 10.3389/fresc.2024.1305925. eCollection 2024. Front Rehabil Sci. 2024. PMID: 38745971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting IL-6 as a novel therapeutic approach for alcohol abstinence - related mechanical allodynia.Neuropharmacology. 2025 Nov 1;278:110584. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2025.110584. Epub 2025 Jun 28. Neuropharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40588184
-
Targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway for chronic pain.Aging Dis. 2024 Feb 1;15(1):186-200. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0515. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 37307838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrathecal non-viral interleukin-10 gene therapy ameliorates neuropathic pain as measured by both classical static allodynia and a novel supra-spinally mediated pain assay, the Two-Arm Rodent Somatosensory (TARS) task.Brain Behav Immun. 2023 Jul;111:177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.04.002. Epub 2023 Apr 8. Brain Behav Immun. 2023. PMID: 37037361 Free PMC article.
-
Valproate attenuates somatic hyperalgesia induced by orofacial inflammation combined with stress through inhibiting spinal IL-6 and STAT1 phosphorylation.Brain Res Bull. 2024 Mar;208:110889. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.110889. Epub 2024 Jan 28. Brain Res Bull. 2024. PMID: 38290590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aniszewska A., Szymanski J., Winnicka M. M., Turlejski K. (2014). Interleukin 6 deficiency affects spontaneous activity of mice in age- and sex-dependent manner. Acta. Neurobiol. Exp. 74 424–432. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

