Genetic variation in ST6GAL1 is a determinant of capecitabine and oxaliplatin induced hand-foot syndrome
- PMID: 35467766
- PMCID: PMC9545609
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.34046
Genetic variation in ST6GAL1 is a determinant of capecitabine and oxaliplatin induced hand-foot syndrome
Abstract
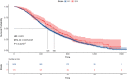
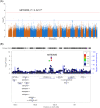
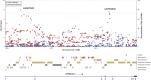
Cancer patients treated with capecitabine and oxaliplatin (XELOX) often develop hand-foot syndrome (HFS) or palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia. Genetic variation in ST6GAL1 is a risk factor for type-2 diabetes (T2D), a disease also associated with HFS. We analysed genome-wide association data for 10 toxicities in advanced colorectal cancer (CRC) patients from the COIN and COIN-B trials. One thousand and fifty-five patients were treated with XELOX ± cetuximab and 745 with folinic acid, fluorouracil and oxaliplatin ± cetuximab. We also analysed rs6783836 in ST6GAL1 with HFS in CRC patients from QUASAR2. Using UK Biobank data, we sought to confirm an association between ST6GAL1 and T2D (17 384 cases, 317 887 controls) and analysed rs6783836 against markers of diabetes, inflammation and psoriasis. We found that 68% of patients from COIN and COIN-B with grade 2-3 HFS responded to treatment as compared to 58% with grade 0-1 HFS (odds ratio [OR] = 1.1, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.02-1.2, P = 2.0 × 10-4 ). HFS was also associated with improved overall survival (hazard ratio = 0.92, 95% CI = 0.84-0.99, P = 4.6 × 10-2 ). rs6783836 at ST6GAL1 was associated with HFS in patients treated with XELOX (OR = 3.1, 95% CI = 2.1-4.6, P = 4.3 × 10-8 ) and was borderline significant in patients receiving capecitabine from QUASAR2, but with an opposite allele effect (OR = 0.66, 95% CI = 0.42-1.03, P = .05). ST6GAL1 was associated with T2D (lead SNP rs3887925, OR = 0.94, 95% CI = 0.92-0.96, P = 1.2 × 10-8 ) and the rs6783836-T allele was associated with lowered HbA1c levels (P = 5.9 × 10-3 ) and lymphocyte count (P = 2.7 × 10-3 ), and psoriasis (P = 7.5 × 10-3 ) beyond thresholds for multiple testing. In conclusion, HFS is a biomarker of treatment outcome and rs6783836 in ST6GAL1 is a potential biomarker for HFS with links to T2D and inflammation.
Keywords: ST6GAL1; XELOX; chemotherapy; colorectal cancer; genetics; toxicity.
© 2022 The Authors. International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
Timothy S. Maughan consults for AstraZeneca and receives personal fees from Pierre Fabre (IDMC services). Timothy S. Maughan received research funding from Merck KgAa and AstraZeneca. The institution where Timothy S. Maughan works receives funding from Bayer. David J. Kerr is a director of Oxford Cancer Biomarkers. All other authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide association studies of toxicity to oxaliplatin and fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy with or without cetuximab in 1800 patients with advanced colorectal cancer.Int J Cancer. 2021 Nov 1;149(9):1713-1722. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33739. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Int J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34270794 Free PMC article.
-
Study protocol of a single-arm phase 2 study evaluating the preventive effect of topical hydrocortisone for capecitabine-induced hand-foot syndrome in colorectal cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy with capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (T-CRACC study).BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Jul 14;22(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02411-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35836104 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacogenetic analyses of 2183 patients with advanced colorectal cancer; potential role for common dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase variants in toxicity to chemotherapy.Eur J Cancer. 2018 Oct;102:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Eur J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30114658 Clinical Trial.
-
Possible Pathways of Capecitabine-Induced Hand-Foot Syndrome.Chem Res Toxicol. 2016 Oct 17;29(10):1591-1601. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00215. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27631426 Review.
-
Prophylactic strategies for hand-foot syndrome/skin reaction associated with systemic cancer treatment: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Support Care Cancer. 2022 Nov;30(11):8655-8666. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-07175-3. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Support Care Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35655045 Review.
Cited by
-
New insights into genetic comorbidity mechanisms: type 2 diabetes and primary open-angle glaucoma.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 16;10(1):e002219. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2025-002219. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40669929 Free PMC article.
-
Topical interventions for preventing hand-foot syndrome resulting from antineoplastic therapy: A scoping review.Rev Esc Enferm USP. 2023 Nov 10;57:e20220107. doi: 10.1590/1980-220X-REEUSP-2023-0107en. eCollection 2023. Rev Esc Enferm USP. 2023. PMID: 37947365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stintzing S, Fischer von Weikersthal L, Vehling‐Kaiser U, et al. Correlation of capecitabine‐induced skin toxicity with treatment efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the German AIO KRK‐0104 trial. Br J Cancer. 2011;105(2):206‐211. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.227 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Diasio R. Oral DPD‐inhibitory fluoropyrimidine drugs ‐ PubMed. Oncology (Williston Park). 2000;14:19‐23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

