MicroRNA-181a-5p prevents the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vivo and in vitro via the MEK1-mediated ERK-MMP signaling pathway
- PMID: 35468097
- PMCID: PMC9085224
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204028
MicroRNA-181a-5p prevents the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vivo and in vitro via the MEK1-mediated ERK-MMP signaling pathway
Abstract
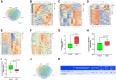
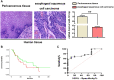
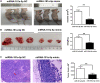
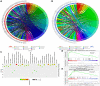
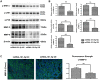
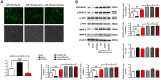
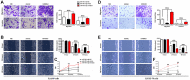
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been revealed to play a crucial role in oncogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). However, the biological role of miR-181a-5p in ESCC is currently less explored. The current study was designed to assess whether miR-181a-5p affects ESCC progression and further investigate relevant underlying mechanisms. Based on the data of GSE161533, GSE17351, GSE75241 and GSE67269 downloaded from GEO database, MAP2K1 (MEK1) was revealed to be one overlapping gene of the top 300 DGEs. Additionally, using the predicting software, miR-181a-5p was projected as the presumed target miRNA. Immunohistochemical staining and RT-qPCR research revealed that miR-181a-5p expression was decreased in human tumor tissues relative to surrounding peri-cancerous tissues. In an in vivo experiment, miR-181a-5p mimics could inhibit tumor growth and metastasis of ESCC. Gene expression profiles in combination with gene ontology (GO) and KEGG pathway analysis revealed that MAP2K1 (MEK1) gene and ERK-MMP pathway were implicated in ESCC progression. MiR-181a-5p mimics inhibited the activity of p-ERK1/2, MMP2 and MMP9 in vivo, as shown by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry labeling. There were no variations in the expression of p-P38 and p-JNK proteins. Additionally, miR-181a-5p mimics lowered p-ERK1/2, MMP2 and MMP9 levels in ECA109 cells, which were restored by MEK1-OE lentivirus. MEK1-OE Lentivirus significantly reversed the function induced by miR-181a-5p mimics in ECA109 cells. Moreover, further investigation indicated that the capability of migration, invasion and proliferation was repressed by miR-181a-5p mimics in ECA109 cells. In short, repressed ERK-MMP pathway mediated by miR-181a-5p can inhibit cell migration, invasion and proliferation by targeting MAP2K1 (MEK1) in ESCC.
Keywords: ESCC; MEK1; miR-181a-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Xu CQ, Zhu ST, Wang M, Guo SL, Sun XJ, Cheng R, Xing J, Wang WH, Shao LL, Zhang ST. Pathway analysis of differentially expressed genes in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015; 19:1652–61. - PubMed
-
- Natsugoe S, Mueller J, Stein HJ, Feith M, Höfler H, Siewert JR. Micrometastasis and tumor cell microinvolvement of lymph nodes from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: frequency, associated tumor characteristics, and impact on prognosis. Cancer. 1998; 83:858–66. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19980901)83:5<858::AID-CNCR9>3.0.CO;2-E - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

