Simultaneous analysis of antigen-specific B and T cells after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination
- PMID: 35468250
- PMCID: PMC9087145
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.24563
Simultaneous analysis of antigen-specific B and T cells after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination
Abstract
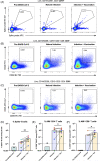
Conventional methods for quantifying and phenotyping antigen-specific lymphocytes can rapidly deplete irreplaceable specimens. This is due to the fact that antigen-specific T and B cells have historically been analyzed in independent assays each requiring millions of cells. A technique that facilitates the simultaneous detection of antigen-specific T and B cells would allow for more thorough immune profiling with significantly reduced sample requirements. To this end, we developed the B and T cell tandem lymphocyte evaluation (BATTLE) assay, which allows for the simultaneous identification of SARS-CoV-2 Spike reactive T and B cells using an activation induced marker (AIM) T cell assay and dual-color B cell antigen probes. Using this assay, we demonstrate that antigen-specific B and T cell subsets can be identified simultaneously using conventional flow cytometry platforms and provide insight into the differential effects of mRNA vaccination on B and T cell populations following natural SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: B cells; SARS-CoV-2; T cells; antigen-specific; natural infection; spike protein; vaccination.
© 2022 The Authors. Cytometry Part A published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Stephen J. Thomas reports compensation from Pfizer, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Merck, Sanofi, Takeda, Themisbio, and Janssen, outside the submitted work. All other authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Altman JD, Moss PA, Goulder PJ, Barouch DH, McHeyzer‐Williams MG, Bell JI, et al. Phenotypic analysis of antigen‐specific T lymphocytes. Science. 1996;274:94–6. - PubMed
-
- Dan JM, Lindestam Arlehamn CS, Weiskopf D, da Silva Antunes R, Havenar‐Daughton C, Reiss SM, et al. A cytokine‐independent approach to identify antigen‐specific human germinal center T follicular helper cells and rare antigen‐specific CD4+ T cells in blood. J Immunol. 2016;1950(197):983–93. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frentsch M, Arbach O, Kirchhoff D, Moewes B, Worm M, Rothe M, et al. Direct access to CD4+ T cells specific for defined antigens according to CD154 expression. Nat Med. 2005;11:1118–24. - PubMed
-
- Kern F, Faulhaber N, Frömmel C, Khatamzas E, Prösch S, Schönemann C, et al. Analysis of CD8 T cell reactivity to cytomegalovirus using protein‐spanning pools of overlapping pentadecapeptides. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:1676–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

