Arbutin Alleviates LPS Induced Sepsis Pneumonia in Mice
- PMID: 35469161
- PMCID: PMC9034914
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5863952
Arbutin Alleviates LPS Induced Sepsis Pneumonia in Mice
Abstract
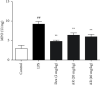
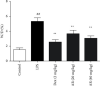
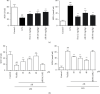
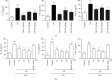
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of arbutin (AR) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sepsis pneumonia. LPS-induced mice and A549 cells were used to establish septic pneumonia model. AR significantly decreased lung wet-to-dry weight (W/D) ratio, lung myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and ameliorated lung histopathological changes. In addition, AR increased super oxide dismutase (SOD) activity, decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) content and levels of cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) in mice. Furthermore, the results demonstrated that AR inhibited the JAK2/STAT3/NF-κB pathway in LPS-induced A549 cells which was further confirmed by siRNA JAK2 experiment. The experimental results indicated that the protective mechanism of AR on sepsis pneumonia might be attributed partly to the inhibition of cytokine production and JAK2/STAT3/NF-κB pathway.
Copyright © 2022 Xiang-Xiang Bian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Biao Y., Chang W., Wu Q. Q., et al. Aucubin protects against tgfbeta1- induced cardiac fibroblasts activation by mediating the AMPKalpha/mTOR signaling pathway. Planta Med . 2018;84(2):91–99. - PubMed
-
- Fusco R., Gugliandolo E., Biundo F., Campolo M., Di Paola R., Cuzzocrea S. Inhibition of inflammasome activation improves lung acute injury induced by carrageenan in a mouse model of pleurisy. FASEB Journal: Official Publication of the Federation of the American Societies for Experimental Biology . 2017;31(8):3497–3511. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601349r. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu H. L., Qian Y. N. Protective effect of propofol combined with ulinastatin on endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology . 2013;29(1):56–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

