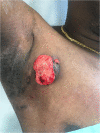
Fast-growing mass in a patient with hidradenitis suppurativa
- PMID: 35470548
- PMCID: PMC9705178
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.13825
Fast-growing mass in a patient with hidradenitis suppurativa
Keywords: fistulae; hidradenitis suppurativa; pyogenic granuloma; squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest
Figures
Comment on
-
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma complicating hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of the prevalence, pathogenesis, and treatment of this dreaded complication.Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018 Mar;27(1):25-28. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018. PMID: 29589641 Review.
References
-
- Daxhelet M, Suppa M, White J, et al. Proposed definitions of typical lesions in hidradenitis Suppurativa. Dermatology. 2020;236(5):431‐438. - PubMed
-
- Valentic JP, Barr RJ, Weinstein GD. Inflammatory neovascular nodules associated with oral isotretinoin treatment of severe acne. Arch Dermatol. 1983;119(10):871‐872. - PubMed
-
- Chapman S, Delgadillo D III, Barber C, Khachemoune A. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma complicating hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of the prevalence, pathogenesis, and treatment of this dreaded complication. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018;27(1):25‐28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical