Paving the way towards effective plant-based inhibitors of hyaluronidase and tyrosinase: a critical review on a structure-activity relationship
- PMID: 35470749
- PMCID: PMC9045780
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2061966
Paving the way towards effective plant-based inhibitors of hyaluronidase and tyrosinase: a critical review on a structure-activity relationship
Abstract
Human has used plants to treat many civilisation diseases for thousands of years. Examples include reserpine (hypertension therapy), digoxin (myocardial diseases), vinblastine and vincristine (cancers), and opioids (palliative treatment). Plants are a rich source of natural metabolites with multiple biological activities, and the use of modern approaches and tools allowed finally for more effective bioprospecting. The new phytochemicals are hyaluronidase (Hyal) inhibitors, which could serve as anti-cancer drugs, male contraceptives, and an antidote against venoms. In turn, tyrosinase inhibitors can be used in cosmetics/pharmaceuticals as whitening agents and to treat skin pigmentation disorders. However, the activity of these inhibitors is stricte dependent on their structure and the presence of the chemical groups, e.g. carbonyl or hydroxyl. This review aims to provide comprehensive and in-depth evidence related to the anti-tyrosinase and anti-Hyal activity of phytochemicals as well as confirming their efficiency and future perspectives.
Keywords: Hyaluronidase; polyphenols; structure–activity relationship; tyrosinase plant-based inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures

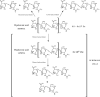

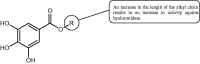
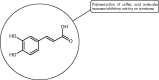

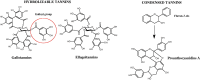



















References
-
- Stafford A, Morris P, Fowler MW.. Plant cell biotechnology: a perspective. Enzyme Microb Technol 1986;8:578–87.
-
- Shakya AK. Medicinal plants: future source of new drugs. Int J Herb Med 2016;4:59–64.
-
- Stranska I, Skalicky M, Novak J, et al. . Analysis of selected poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) cultivars: pharmaceutically important alkaloids. Ind Crop Prod 2013;41:120–6.
-
- Li Y, Gao Z, Piao C, et al. . A stable and efficient Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of the medicinal plant Digitalis purpurea L. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2014;172:1807–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
