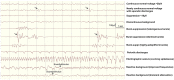
EEG monitoring after cardiac arrest
- PMID: 35471582
- PMCID: PMC9468095
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-022-06697-y
EEG monitoring after cardiac arrest
Conflict of interest statement
CS is Associate Editor of Intensive Care Medicine. The other authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hirsch LJ, Fong MWK, Leitinger M, LaRoche SM, Beniczky S, Abend NS, Lee JW, Wusthoff CJ, Hahn CD, Westover MB, Gerard EE, Herman ST, Haider HA, Osman G, Rodriguez-Ruiz A, Maciel CB, Gilmore EJ, Fernandez A, Rosenthal ES, Claassen J, Husain AM, Yoo JY, So EL, Kaplan PW, Nuwer MR, van Putten M, Sutter R, Drislane FW, Trinka E, Gaspard N. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s standardized critical care EEG terminology: 2021 version. J Clin Neurophysiol Off Publ Am Electroencephalogr Soc. 2021;38:1–29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sandroni C, D’Arrigo S, Cacciola S, Hoedemaekers CWE, Westhall E, Kamps MJA, Taccone FS, Poole D, Meijer FJA, Antonelli M, Hirsch KG, Soar J, Nolan JP, Cronberg T. Prediction of good neurological outcome in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: a systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2022;48:389–413. doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06618-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Westhall E, Rosen I, Rundgren M, Bro-Jeppesen J, Kjaergaard J, Hassager C, Lindehammar H, Horn J, Ullen S, Nielsen N, Friberg H, Cronberg T. Time to epileptiform activity and EEG background recovery are independent predictors after cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol Off J Int Fed Clin Neurophysiol. 2018;129:1660–1668. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.05.016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical