Mammalian antiviral RNAi is on the move
- PMID: 35471636
- PMCID: PMC9156964
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.2022111210
Mammalian antiviral RNAi is on the move
Abstract
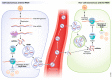
Recent work reported the existence of a mammalian cell-autonomous antiviral defence based on RNA interference (RNAi), which relies on the accumulation of virus-derived small interfering RNAs (vsiRNAs) to guide the degradation of complementary viral RNAs. In a new study, Zhang et al (2022) find that, in infected mice, vsiRNAs can enter the bloodstream via their incorporation into extracellular vesicles (EVs) and confer sequence-specific antiviral activity to recipient cells, thus indicating that mammalian antiviral RNAi participates in both cell-autonomous and non-cell-autonomous host defence.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Guo Z, Li Y, Ding SW (2019) Small RNA‐based antimicrobial immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 19: 31–44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

