Highlight selection of radiochemistry and radiopharmacy developments by editorial board
- PMID: 35471681
- PMCID: PMC9043146
- DOI: 10.1186/s41181-022-00162-3
Highlight selection of radiochemistry and radiopharmacy developments by editorial board
Abstract
Background: The Editorial Board of EJNMMI Radiopharmacy and Chemistry releases a biyearly highlight commentary to update the readership on trends in the field of radiopharmaceutical development.
Results: This commentary of highlights has resulted in 23 different topics selected by each member of the Editorial Board addressing a variety of aspects ranging from novel radiochemistry to first in man application of novel radiopharmaceuticals and also a contribution in relation to MRI-agents is included.
Conclusion: Trends in (radio)chemistry and radiopharmacy are highlighted demonstrating the progress in the research field being the scope of EJNMMI Radiopharmacy and Chemistry.
Keywords: Highlights; Radiochemistry; Radiopharmacy; Review.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have competing interests.
Figures




References
-
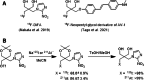
- Chen M, Chen Z, Castillo JB, Cui L, Zhou K, Shen B, Xie J, Chin FT, Rao J. [18F]-C-SNAT4: an improved caspase-3-sensitive nanoaggregation PET tracer for imaging of tumor responses to chemo- and immunotherapies. EJNMMI. 2021;48:3386–3399. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Zhao L, Ruan D, Pang Y, Hao B, Dai Y, et al. Usefulness of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in patients presenting with inconclusive [18F]FDG PET/CT findings. EJNMMI. 2021;48:73–86. - PubMed
