Exploring the Reactivity of B-Connected Carboranylphosphines in Frustrated Lewis Pair Chemistry: A New Frame for a Classic System
- PMID: 35472172
- PMCID: PMC9320892
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202200531
Exploring the Reactivity of B-Connected Carboranylphosphines in Frustrated Lewis Pair Chemistry: A New Frame for a Classic System
Abstract
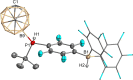
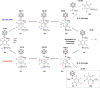
The primary phosphines MesPH2 and tBuPH2 react with 9-iodo-m-carborane yielding B9-connected secondary carboranylphosphines 1,7-H2 C2 B10 H9 -9-PHR (R=2,4,6-Me3 C6 H2 (Mes; 1 a), tBu (1 b)). Addition of tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane (BCF) to 1 a, b resulted in the zwitterionic compounds 1,7-H2 C2 B10 H9 -9-PHR(p-C6 F4 )BF(C6 F5 )2 (2 a, b) through nucleophilic para substitution of a C6 F5 ring followed by fluoride transfer to boron. Further reaction with Me2 SiHCl prompted a H-F exchange yielding the zwitterionic compounds 1,7-H2 C2 B10 H9 -9-PHR(p-C6 F4 )BH(C6 F5 )2 (3 a, b). The reaction of 2 a, b with one equivalent of R'MgBr (R'=Me, Ph) gave the extremely water-sensitive frustrated Lewis pairs 1,7-H2 C2 B10 H9 -9-PR(p-C6 F4 )B(C6 F5 )2 (4 a, b). Hydrolysis of the B-C6 F4 bond in 4 a, b gave the first tertiary B-carboranyl phosphines with three distinct substituents, 1,7-H2 C2 B10 H9 -9-PR(p-C6 F4 H) (5 a, b). Deprotonation of the zwitterionic compounds 2 a, b and 3 a, b formed anionic phosphines [1,7-H2 C2 B10 H9 -9-PR(p-C6 F4 )BX(C6 F5 )2 ]- [DMSOH]+ (R=Mes, X=F (6 a), R=tBu, X=F (6 b); R=Mes, X=H (7 a), R=tBu, X=H (7 b)). Reaction of 2 a, b with an excess of Grignard reagents resulted in the addition of R' at the boron atom yielding the anions [1,7-H2 C2 B10 H9 -9-PR(p-C6 F4 )BR'(C6 F5 )2 ]- (R=Mes, R'=Me (8 a), R=tBu, R'=Me (8 b); R=Mes, R'=Ph (9 a), R=tBu, R'=Ph (9 b)) with [MgBr(Et2 O)n ]+ as counterion. The ability of the zwitterionic compounds 3 a, b to hydrogenate imines as well as the Brønsted acidity of 3 a were investigated.
Keywords: anions; carboranes; dihydrogen activation; frustrated Lewis pairs; phosphorus; zwitterions.
© 2022 The Authors. Chemistry - A European Journal published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ligand versus Complex: C-F and C-H Bond Activation of Polyfluoroaromatics at a Cyclic (Alkyl)(Amino)Carbene.Chemistry. 2017 Mar 17;23(16):3993-4009. doi: 10.1002/chem.201605950. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28139870
-
New Reactivity Patterns in 3H-Phosphaallene Chemistry [Aryl-P=C=C(H)-tBu]: Hydroboration of the C=C Bond, Deprotonation and Trimerisation.Chemistry. 2020 Dec 4;26(68):15977-15988. doi: 10.1002/chem.202002506. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Chemistry. 2020. PMID: 32618025 Free PMC article.
-
Complexation and Versatile Reactivity of a Highly Lewis Acidic Cationic Mg Complex with Alkynes and Phosphines.Chemistry. 2019 Feb 6;25(8):2025-2034. doi: 10.1002/chem.201804802. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Chemistry. 2019. PMID: 30431191
-
Germanium Analogue of the Parent Phosphine-Borane FLP Compound.Chem Asian J. 2023 Nov 2;18(21):e202300747. doi: 10.1002/asia.202300747. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Chem Asian J. 2023. PMID: 37739931
-
The Non-Ancillary Nature of Trimethylsilylamide Substituents in Boranes and Borinium Cations.Chemistry. 2022 May 11;28(27):e202200698. doi: 10.1002/chem.202200698. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Chemistry. 2022. PMID: 35262980 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hydrogen Activation by Frustrated and Not So Frustrated Lewis Pairs Based on Pyramidal Lewis Acid 9-Boratriptycene: A Computational Study.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 15;7(51):48493-48505. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06836. eCollection 2022 Dec 27. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36591180 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

