Colorimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 by uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP)
- PMID: 35472524
- PMCID: PMC9035611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.04.036
Colorimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 by uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP)
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Colorimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 by uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP)" [International Journal of Infectious Diseases 120 (2023) Pages 132-134].Int J Infect Dis. 2023 Nov;136:91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2023.09.011. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Int J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37774600 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objectives: Preventing reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) carryover contamination could be solved by adding deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) and uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) into the reaction master mix.
Methods: RNA was extracted from nasopharyngeal swab samples by a simple RNA extraction method.
Results: Testing of 77 samples demonstrated 91.2% sensitivity (95% confidence interval [CI]: 78-98.2%) and 100% specificity (95% confidence interval: 92-100%) using UDG RT-LAMP.
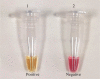
Conclusion: This colorimetric UDG RT-LAMP is a simple-to-use, fast, and easy-to-interpret method, which could serve as an alternative for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, especially in remote hospitals and laboratories with under-equipped medical facilities.
Keywords: Carryover contamination; RT-LAMP; SARS-CoV-2; UDG; dUTP.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Hsieh K, Mage PL, Csordas AT, Eisenstein M, Soh HT. Simultaneous elimination of carryover contamination and detection of DNA with uracil-DNA-glycosylase-supplemented loop-mediated isothermal amplification (UDG-LAMP) Chem Commun (Camb) 2014;50:3747–3749. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous