Global, regional, and national burden of hypertensive heart disease during 1990-2019: an analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019
- PMID: 35473603
- PMCID: PMC9044894
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-022-13271-0
Global, regional, and national burden of hypertensive heart disease during 1990-2019: an analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019
Abstract
Background: Hypertensive heart disease (HHD) is a major public health issue worldwide. We analyzed the global, regional, and national burden of HHD between the years 1990 and 2019 in relation to age, gender, and socioeconomic factors.
Methods: The prevalence and death rates, the disability adjusted life-years (DALY), and the corresponding age-standardized rates of HHD were extracted from the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. The epidemiological trends were evaluated by calculating the estimated annual percentage changes (EAPC) of the above variates.
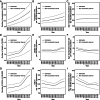
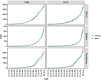
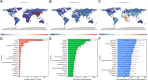
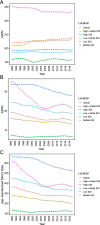
Results: A total of 19.60 million HHD cases were documented in 2019 compared to 7.82 million in 1990, corresponding to an EAPC of 0.17. Contrarily, the global age-standardized death rate (ASDR) and age-standardized DALYs decreased with respective EAPCs of - 0.74 and - 1.02. HHD mostly occurred in people aged over 65. The disease burden of HHD varied considerably between countries, and univariate linear regression indicated that many socioeconomic variables had significantly negative correlations with age-standardized DALY rate.
Conclusion: HHD cases have increased over the last three decades; however the mortality rate has declined. Multi-faceted improvements in health, education and income could help to alleviate the disease burden of HHD, specially in some regions with lower socio-demographic index and higher ASDR.
Keywords: Global disease burden; Hypertensive heart disease; Socioeconomic factors; Time trends.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Gidding SS, Liu K, Colangelo LA, Cook NL, Goff DC, Glasser SP, Gardin JM, Lima JA. Longitudinal determinants of left ventricular mass and geometry: the coronary artery risk development in young adults (CARDIA) study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6(5):769–775. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.112.000450. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McManus DD, Xanthakis V, Sullivan LM, Zachariah J, Aragam J, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Vasan RS. Longitudinal tracking of left atrial diameter over the adult life course: clinical correlates in the community. Circulation. 2010;121(5):667–674. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.885806. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Omidi N, Arabloo J, Rezapour A, Alaeddini F, Bragazzi NL, Pourasghari H, Behzadifar M, Salarifar M, Khorgami M, Ghorashi SM, et al. Burden of hypertensive heart disease in Iran during 1990-2017: findings from the global burden of disease study 2017. PLoS One. 2021;16(9):e0257617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257617. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE, Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, DePalma SM, Gidding S, Jamerson KA, Jones DW, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71(6):e13–e115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

