Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 drives glioma progression by modulating the serotonin/L1CAM/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 35473609
- PMCID: PMC9044587
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09569-2
Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 drives glioma progression by modulating the serotonin/L1CAM/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
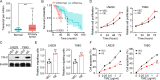
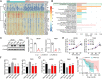
Background: Glioma is one of the main causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide and is associated with high heterogeneity. However, the key players determining the fate of glioma remain obscure. In the present study, we shed light on tumor metabolism and aimed to investigate the role of tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (TPH-1) in the advancement of glioma.
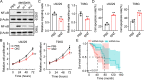
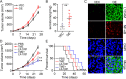
Method: Herein, the levels of TPH-1 expression in glioma tissues were evaluated using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Further, the proliferative characteristics and migration ability of TPH-1 overexpressing LN229/T98G cells were evaluated. Additionally, we performed a cytotoxicity analysis using temozolomide (TMZ) in these cells. We also examined the tumor growth and survival time in a mouse model of glioma treated with chemotherapeutic agents and a TPH-1 inhibitor.
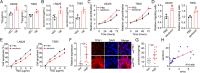
Results: The results of both clinical and experimental data showed that excess TPH-1 expression resulted in sustained glioma progression and a dismal overall survival in these patients. Mechanistically, TPH-1 increased the production of serotonin in glioma cells. The elevated serotonin levels then augmented the NF-κB signaling pathway through the upregulation of the L1-cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM), thereby contributing to cellular proliferation, invasive migration, and drug resistance. In vivo experiments demonstrated potent antitumor effects, which benefited further from the synergistic combination of TMZ and LX-1031.
Conclusion: Taken together, these data suggested that TPH-1 facilitated cellular proliferation, migration, and chemoresistance in glioma through the serotonin/L1CAM/NF-κB pathway. By demonstrating the link of amino acid metabolic enzymes with tumor development, our findings may provide a potentially viable target for therapeutic manipulation aimed at eradicating glioma.
Keywords: Glioma; L1CAM; Serotonin; TPH-1.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Xu S, Tang L, Li X, et al. Immunotherapy for glioma: current management and future application. Cancer Lett. 2020;476. 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.02.002. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

