The multifaceted role of kidney tubule mitochondrial dysfunction in kidney disease development
- PMID: 35473814
- PMCID: PMC9464682
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2022.03.012
The multifaceted role of kidney tubule mitochondrial dysfunction in kidney disease development
Abstract
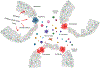
More than 800 million people suffer from kidney disease. Genetic studies and follow-up animal models and cell biological experiments indicate the key role of proximal tubule metabolism. Kidneys have one of the highest mitochondrial densities. Mitochondrial biogenesis, mitochondrial fusion and fission, and mitochondrial recycling, such as mitophagy are critical for proper mitochondrial function. Mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to an energetic crisis, orchestrate different types of cell death (apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, and ferroptosis), and influence cellular calcium levels and redox status. Collectively, mitochondrial defects in renal tubules contribute to epithelial atrophy, inflammation, or cell death, orchestrating kidney disease development.
Keywords: cell death; inflammation; kidney disease; mitochondria; mitophagy; renal tubule cell.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
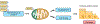


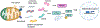
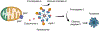
References
-
- Zhong F et al. (2019) Emerging Role of Mitochondrial DNA as a Major Driver of Inflammation and Disease Progression. Trends Immunol 40 (12), 1120–1133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

