Contribution of the histone variant H2A.Z to expression of responsive genes in plants
- PMID: 35474148
- PMCID: PMC9588091
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.04.006
Contribution of the histone variant H2A.Z to expression of responsive genes in plants
Abstract
The histone variant H2A.Z plays a critical role in chromatin-based processes such as transcription, replication, and repair in eukaryotes. Although many H2A.Z-associated processes and features are conserved in plants and animals, a distinguishing feature of plant chromatin is the enrichment of H2A.Z in the bodies of genes that exhibit dynamic expression, particularly in response to differentiation and the environment. Recent work sheds new light on the plant machinery that enables dynamic changes in H2A.Z enrichment and identifies additional chromatin-based pathways that contribute to transcriptional properties of H2A.Z-enriched chromatin. In particular, analysis of a variety of responsive loci reveals a repressive role for H2A.Z in expression of responsive genes and identifies roles for SWR1 and INO80 chromatin remodelers in enabling dynamic regulation of H2A.Z levels and transcription. These studies lay the groundwork for understanding how this ancient histone variant is harnessed by plants to enable responsive and dynamic gene expression (Graphical Abstract).
Keywords: Chromatin; H2A.Z; H3K27me3; INO80 subfamily of remodelers; Stress response; Transcriptional repression.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

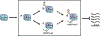
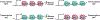
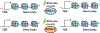
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional regulation of autophagy by chromatin remodeling complex and histone variant.Autophagy. 2023 Oct;19(10):2824-2826. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2200352. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 37039545 Free PMC article.
-
Variation on a theme: Evolutionary strategies for H2A.Z exchange by SWR1-type remodelers.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021 Jun;70:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.10.014. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33217681 Review.
-
Roles of the INO80 and SWR1 Chromatin Remodeling Complexes in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 17;20(18):4591. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184591. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31533258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NAP1-RELATED PROTEIN1 and 2 negatively regulate H2A.Z abundance in chromatin in Arabidopsis.Nat Commun. 2020 Jun 8;11(1):2887. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16691-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32513971 Free PMC article.
-
Global regulation of H2A.Z localization by the INO80 chromatin-remodeling enzyme is essential for genome integrity.Cell. 2011 Jan 21;144(2):200-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.021. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21241891 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
H2A.Z removal mediates the activation of genes accounting for cell elongation under light and temperature stress.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Nov 19;43(12):286. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03366-w. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39562374 Review.
-
Nematode histone H2A variant evolution reveals diverse histories of retention and loss and evidence for conserved core-like variant histone genes.PLoS One. 2024 May 30;19(5):e0300190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300190. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38814971 Free PMC article.
-
Histone variants shape chromatin states in Arabidopsis.Elife. 2023 Jul 19;12:RP87714. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87714. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37467143 Free PMC article.
-
The master growth regulator DELLA binding to histone H2A is essential for DELLA-mediated global transcription regulation.Nat Plants. 2023 Aug;9(8):1291-1305. doi: 10.1038/s41477-023-01477-y. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Nat Plants. 2023. PMID: 37537399 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional histone variants in genome function.Nat Rev Genet. 2025 Feb;26(2):82-104. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00759-1. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Nat Rev Genet. 2025. PMID: 39138293 Review.
References
-
- Kornberg RD, Structure of chromatin, Annu Rev Biochem 46 (1977) 931–54. - PubMed
-
- Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ, Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution, Nature 389(6648) (1997) 251–60. - PubMed
-
- Talbert PB, Ahmad K, Almouzni G, Ausio J, Berger F, Bhalla PL, Bonner WM, Cande WZ, Chadwick BP, Chan SW, Cross GA, Cui L, Dimitrov SI, Doenecke D, Eirin-Lopez JM, Gorovsky MA, Hake SB, Hamkalo BA, Holec S, Jacobsen SE, Kamieniarz K, Khochbin S, Ladurner AG, Landsman D, Latham JA, Loppin B, Malik HS, Marzluff WF, Pehrson JR, Postberg J, Schneider R, Singh MB, Smith MM, Thompson E, Torres-Padilla ME, Tremethick DJ, Turner BM, Waterborg JH, Wollmann H, Yelagandula R, Zhu B, Henikoff S, A unified phylogeny-based nomenclature for histone variants, Epigenetics Chromatin 5 (2012) 7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Talbert PB, Henikoff S, Histone variants on the move: substrates for chromatin dynamics, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(2) (2017) 115–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

