Inequality and cooperation in social networks
- PMID: 35474324
- PMCID: PMC9042846
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-10733-8
Inequality and cooperation in social networks
Abstract
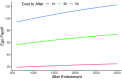
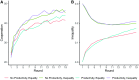
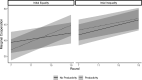
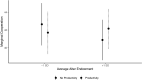
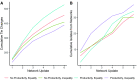
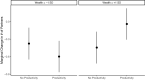
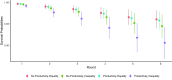
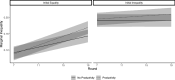
Social networks are fundamental to the broad scale cooperation observed in human populations. But by structuring the flow of benefits from cooperation, networks also create and sustain macro-level inequalities. Here we ask how two aspects of inequality shape the evolution of cooperation in dynamic social networks. Results from a crowdsourced experiment (N = 1080) show that inequality alters the distribution of cooperation within networks such that participants engage in more costly cooperation with their wealthier partners in order to maintain more valuable connections to them. Inequality also influences network dynamics, increasing the tendency for participants to seek wealthier partners, resulting in structural network change. These processes aggregate to alter network structures and produce greater system-level inequality. The findings thus shed critical light on how networks serve as both boon and barrier to macro-level human flourishing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The emergence of inequality in social groups: Network structure and institutions affect the distribution of earnings in cooperation games.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 20;13(7):e0200965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200965. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30028884 Free PMC article.
-
Contagion of Cooperation in Static and Fluid Social Networks.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 19;8(6):e66199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066199. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840422 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation, clustering, and assortative mixing in dynamic networks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 30;115(5):951-956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715357115. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29339478 Free PMC article.
-
Networks of reliable reputations and cooperation: a review.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;376(1838):20200297. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0297. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34601917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Social structure and the evolutionary ecology of inequality.Trends Cogn Sci. 2025 Feb;29(2):201-213. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2024.10.013. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Trends Cogn Sci. 2025. PMID: 39632153 Review.
Cited by
-
Opinion dynamics in financial markets via random networks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Dec 6;119(49):e2201573119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201573119. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36445969 Free PMC article.
-
A reinforcement learning approach to explore the role of social expectations in altruistic behavior.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 31;13(1):1717. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28659-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36720949 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency and resilience of cooperation in asymmetric social dilemmas.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 5;121(10):e2315558121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315558121. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38408249 Free PMC article.
-
Inequality and fairness with heterogeneous endowments.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 31;17(10):e0276864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276864. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36315514 Free PMC article.
-
Reputations for treatment of outgroup members can prevent the emergence of political segregation in cooperative networks.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 24;14(1):7721. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43486-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38001105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DiMaggio P, Garip F. Network effects and social inequality. Ann. Rev. Sociol. 2012;38:93–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.soc.012809.102545. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

