Emerging Electrochemical Biosensing Trends for Rapid Diagnosis of COVID-19 Biomarkers as Point-of-Care Platforms: A Critical Review
- PMID: 35474766
- PMCID: PMC9026073
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00638
Emerging Electrochemical Biosensing Trends for Rapid Diagnosis of COVID-19 Biomarkers as Point-of-Care Platforms: A Critical Review
Abstract
Rapid diagnosis is a critical aspect associated with controlling the spread of COVID-19. Electrochemical sensor platforms are ideally suited for rapid and highly sensitive detection of biomolecules. This review focuses on state-of-the-art of COVID-19 biomarker detection by utilizing electrochemical biosensing platforms. Point-of-care (POC) sensing is one of the most promising and emerging fields in detecting and quantifying health biomarkers. Electrochemical biosensors play a major role in the development of point-of-care devices because of their high sensitivity, specificity, and ability for rapid analysis. Integration of electrochemistry with point-of-care technologies in the context of COVID-19 diagnosis and screening has facilitated in convenient operation, miniaturization, and portability. Identification of potential biomarkers in disease diagnosis is crucial for patient monitoring concerning severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). In this review, we will discuss the choice of biomarkers in addition to the various types of electrochemical sensors that have been developed to meet the needs of rapid detection and disease severity analysis.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): S. Prasad and S. Muthukumar have a significant interest in EnLiSense LLC, a company that may have a commercial interest in the results of this research and technology. The potential individual conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by The University of Texas at Dallas and played no role in the study design, in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, in the writing of the report, or in the decision to submit the report for publication.
Figures

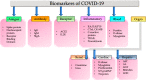



References
-
- WHO . WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Covid19.Who.Int.
-
- Samper I. C.; Sánchez-Cano A.; Khamcharoen W.; Jang I.; Siangproh W.; Baldrich E.; Geiss B. J.; Dandy D. S.; Henry C. S. Electrochemical Capillary-Flow Immunoassay for Detecting Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Antibodies at the Point of Care. ACS Sensors 2021, 6 (11), 4067–4075. 10.1021/acssensors.1c01527. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Madhurantakam S.; Karnam J. B.; Brabazon D.; Takai M.; Ahad I. U.; Balaguru Rayappan J. B.; Krishnan U. M. Nano”: An Emerging Avenue in Electrochemical Detection of Neurotransmitters. ACS Chemical Neuroscience 2020, 11, 4024–4047. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

