Autologous humanized mouse models of iPSC-derived tumors enable characterization and modulation of cancer-immune cell interactions
- PMID: 35474871
- PMCID: PMC9017190
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2021.100153
Autologous humanized mouse models of iPSC-derived tumors enable characterization and modulation of cancer-immune cell interactions
Abstract
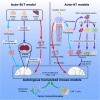
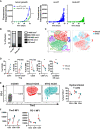
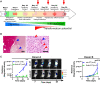
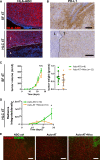
Modeling the tumor-immune cell interactions in humanized mice is complex and limits drug development. Here, we generated easily accessible tumor models by transforming either primary skin fibroblasts or induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cell lines injected in immune-deficient mice reconstituted with human autologous immune cells. Our results showed that fibroblastic, hepatic, or neural tumors were all efficiently infiltrated and partially or totally rejected by autologous immune cells in humanized mice. Characterization of tumor-immune infiltrates revealed high expression levels of the dysfunction markers Tim3 and PD-1 in T cells and an enrichment in regulatory T cells, suggesting rapid establishment of immunomodulatory phenotypes. Inhibition of PD-1 by Nivolumab in humanized mice resulted in increased immune cell infiltration and a slight decrease in tumor growth. We expect that these versatile and accessible cancer models will facilitate preclinical studies and the evaluation of autologous cancer immunotherapies across a range of different tumor cell types.
Keywords: PD-1; autologous tumors; cancer immunotherapy; humanized mouse models; iPSC.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. C.R. and M.P. are co-founders, shareholders, and officers of the regenerative medicine company Morphocell Technologies, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Ashizawa T., Iizuka A., Nonomura C., Kondou R., Maeda C., Miyata H., Sugino T., Mitsuya K., Hayashi N., Nakasu Y., et al. Antitumor effect of programmed death-1 (PD-1) blockade in humanized the NOG-MHC double knockout mouse. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017;23:149–158. - PubMed
-
- Balmain A., Harris C.C. Carcinogenesis in mouse and human cells: parallels and paradoxes. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:371–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

