Deficient DNASE1L3 facilitates neutrophil extracellular traps-induced invasion via cyclic GMP-AMP synthase and the non-canonical NF-κB pathway in diabetic hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 35474906
- PMCID: PMC9021716
- DOI: 10.1002/cti2.1386
Deficient DNASE1L3 facilitates neutrophil extracellular traps-induced invasion via cyclic GMP-AMP synthase and the non-canonical NF-κB pathway in diabetic hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: Diabetic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients have high mortality and metastasis rates. Diabetic conditions promote neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) generation, which mediates HCC metastasis and invasion. However, whether and how diabetes-induced NETs trigger HCC invasion is largely unknown. Here, we aimed to observe the effects of diabetes-induced NETs on HCC invasion and investigate mechanisms relevant to a DNA sensor cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS).
Methods: Serum from diabetic patients and healthy individuals was collected. Human neutrophil-derived NETs were isolated for stimulating HCC cell invasion. Data from the SEER and TCGA databases were used for bioinformatics analysis. In HCC cells and allograft models, NETs-triggered invasion was observed.
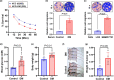
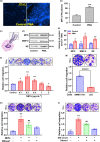
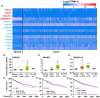
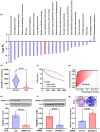
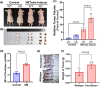
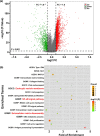
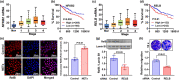
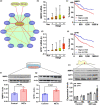
Results: Diabetic HCC patients had poorer survival than non-diabetic ones. Either diabetic serum or extracted NETs caused HCC invasion. Induction of diabetes or NETosis elicited HCC allograft invasion in nude mice. HCC cell invasion was attenuated by the treatment with DNase1. In TCGA_LIHC, an extracellular DNase DNASE1L3 was downregulated in tumor tissues, while function terms (the endocytic vesicle membrane, the NF-κB pathway and extracellular matrix disassembly) were enriched. DNASE1L3 knockdown in LO2 hepatocytes or H22 cell-derived allografts facilitated HCC invasion in NETotic or diabetic nude mice. Moreover, exposure of HCC cells to NETs upregulated cGAS and the non-canonical NF-κB pathway and induced expression of metastasis genes (MMP9 and SPP1). Both cGAS inhibitor and NF-κB RELB knockdown diminished HCC invasion caused by NETs DNA. Also, cGAS inhibitor was able to retard translocation of NF-κB RELB.
Conclusion: Defective DNASE1L3 aggravates NETs DNA-triggered HCC invasion on diabetic conditions via cGAS and the non-canonical NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: cyclic GMP‐AMP synthase; diabetes; hepatocellular carcinoma; metastasis; neutrophil extracellular traps; non‐canonical NF‐κB pathway.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical & Translational Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) Promote Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Metastasis by Suppressing lncRNA MIR503HG to Activate the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway.Front Immunol. 2022 May 30;13:867516. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867516. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35707534 Free PMC article.
-
PPARα suppresses growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in a high-fat diet context by reducing neutrophil extracellular trap release.JHEP Rep. 2024 Sep 30;7(1):101228. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2024.101228. eCollection 2025 Jan. JHEP Rep. 2024. PMID: 39802808 Free PMC article.
-
The cytosolic DNA sensor cGAS recognizes neutrophil extracellular traps.Sci Signal. 2021 Mar 9;14(673):eaax7942. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aax7942. Sci Signal. 2021. PMID: 33688080
-
Who and how, DNA sensors in NETs-driven inflammation.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 28;14:1190177. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1190177. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37187738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Formation of NETs and Their Mechanism of Promoting Tumor Metastasis.J Oncol. 2023 Mar 11;2023:7022337. doi: 10.1155/2023/7022337. eCollection 2023. J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36942262 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The emerging role of neutrophil extracellular traps in ulcerative colitis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1425251. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425251. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39170617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate deep vein thrombosis: from mechanism to therapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 23;14:1198952. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1198952. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37680629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constructing a prognostic model for hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatics analysis of inflammation-related genes.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 11;11:1420353. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1420353. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39055701 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of interactomic hub genes in PBMC cells in type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and periodontitis.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Mar 26;24(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04041-y. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38532421 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NETs) Degradation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 3;24(5):4896. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054896. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
