Event Rates and Risk Factors for Recurrent Cardiovascular Events and Mortality in a Contemporary Post Acute Coronary Syndrome Population Representing 239 234 Patients During 2005 to 2018 in the United States
- PMID: 35475346
- PMCID: PMC9238606
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022198
Event Rates and Risk Factors for Recurrent Cardiovascular Events and Mortality in a Contemporary Post Acute Coronary Syndrome Population Representing 239 234 Patients During 2005 to 2018 in the United States
Abstract
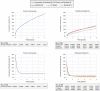
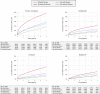
Background Patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) are recognized by guidelines as remaining at high risk for adverse outcomes. Evidence from contemporary, representative ACS populations in a clinical practice setting is necessary to identify subgroups and strategies for improving patient outcomes. We aimed to describe event rates and risk factors in an ACS population over prolonged follow-up for cardiovascular end points. Methods and Results We identified 239 234 patients in the Optum Research Database (57.2% men; mean [standard deviation] age, 69.2 [12.2] years) with evidence of an ACS hospitalization (index ACS) during January 1, 2005 through December 30, 2018. Subgroups were based on index ACS event (myocardial infarction/unstable angina and revascularization status) and the Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction Risk Score for Secondary Prevention. The 5-year event rate for the primary end point representing nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal ischemic stroke, and cardiovascular death was 33.4% (95% CI, 33.1%-33.7%; P<0.001). The risk of experiencing the primary end point was ≈6-fold higher immediately after discharge (≈40.9% annualized risk) as compared with the period 1+ years after hospitalization (≈6.4% annualized risk). Among subgroups, the 5-year primary end point event rate was highest for myocardial infarction without revascularization and a Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction Risk Score for Secondary Prevention ≥4, at 47.9% (95% CI, 47.3%-48.4%; P<0.001) and 56.7% (95% CI, 55.9%-57.4%; P<0.001), respectively. Conclusions Patients with ACS remain at very high risk of experiencing recurrent cardiovascular events, particularly early after discharge, with identifiable subgroups at multifold higher risk of specific clinical end points.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; cardiovascular events; risk factor; risk stratification.
Figures


References
-
- O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey DE, Chung MK, de Lemos JA, Ettinger SM, Fang JC, Fesmire FM, Franklin BA, et al.; American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines . 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST‐elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013;127:e362–e425. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182742cf6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, Casey DE Jr, Ganiats TG, Holmes DR Jr, Jaffe AS, Jneid H, Kelly RF, Kontos MC, et al.; ACC/AHA Task Force Members . 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non‐ST‐elevation acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;130:e344–e426. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000134. Epub 2014. Erratum in: Circulation. 2014;130:e433–4. Dosage error in article text. PMID: 25249585. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, Antunes MJ, Bucciarelli‐Ducci C, Bueno H, Caforio ALP, Crea F, Goudevenos JA, Halvorsen S, et al.; ESC Scientific Document Group . 2017 ESC guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST‐segment elevation. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:119–177. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx393 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, Braun LT, de Ferranti S, Faiella‐Tommasino J, Forman DE, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;139:e1082–e1143. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000625. Epub 2018. Erratum in: Circulation. 2019;139:e1182‐e1186. PMID: 30586774; PMCID: PMC7403606. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

