Early life programming of health and disease: The long-term consequences of obesity in pregnancy
- PMID: 35475555
- PMCID: PMC9540012
- DOI: 10.1111/jhn.13023
Early life programming of health and disease: The long-term consequences of obesity in pregnancy
Abstract
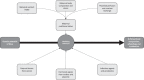
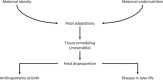
The prevalence of overweight and obesity is rising in all parts of the world and, among young women, it presents a very clear danger during pregnancy. Women who are overweight or who gain excessive weight during pregnancy are at greater risk of complications in pregnancy and labour, and are more likely to lose their child to stillbirth or die themselves during pregnancy. This narrative review considers the evidence that, in addition to increasing risk of poor pregnancy outcomes, obesity has the capacity to programme foetuses to be at greater risk of cardiometabolic disorders later in life. An extensive body of evidence from prospective and retrospective cohorts, as well as record linkage studies, demonstrates associations of maternal obesity and/or gestational diabetes with cardiovascular disease, as well as type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Studies in animals suggest that these associations are underpinned by adaptations that occur in foetal life, which remodel the structures of major organs, including the brain, kidney and pancreas.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; diabetes; disease; life phase; obesity; pregnancy; therapeutic areas.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Dietetic Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Keys A, Anderson JT, Grande F. Serum cholesterol response to changes in the diet: II. The effect of cholesterol in the diet. Metabolism. 1965;14:759–65. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. The low‐density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. - PubMed
-
- Calder PC, Carding SR, Christopher G, Kuh D, Langley‐Evans SC, McNulty H. A holistic approach to healthy ageing: how can people live longer, healthier lives? J Hum Nutr Diet. 2018;31:439–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

