Ulinastatin alleviates early brain injury after traumatic brain injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis
- PMID: 35475892
- PMCID: PMC9020790
- DOI: 10.1590/acb370108
Ulinastatin alleviates early brain injury after traumatic brain injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis
Abstract
Purpose: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains a major public health problem and cause of death. Ulinastatin (UTI), a serine protease inhibitor, has been reported to have an anti-inflammatory effect and play a role in immunoregulation and organ protection by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, oxidative stress and inflammation. However, the neuroprotective of UTI in TBI has not been confirmed. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the neuroprotection and potential molecular mechanisms of UTI in TBI-induced EBI in a C57BL/6 mouse model.
Methods: The neurological score and brain water content were evaluated. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect neuroinflammatory cytokine levels, ROS and malondialdehyde detection to evaluate oxidative stress levels, and TUNEL staining and western blotting to examine neuronal damages and their related mechanisms.
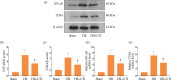
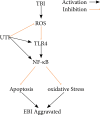
Results: Treatment with UTI markedly increased the neurological score; alleviated brain oedema; decreased the inflammatory cytokine tumour necrosis factor a, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6 and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) levels; inhibited oxidative stress; decreased caspase-3 and Bax protein expressions; and increased the Bcl-2 levels, indicating that UTI-mediated inhibition of neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis ameliorated neuronal death after TBI. The neuroprotective capacity of UTI is partly dependent on the TLR4/NF-kB/p65 signalling pathway.
Conclusions: Therefore, this study reveals that UTI improves neurological outcomes in mice and reduces neuronal death by protecting against neural neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Nothing to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ulinastatin alleviates early brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via ROS/MAPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway.Acta Cir Bras. 2022 Sep 5;37(6):e370606. doi: 10.1590/acb370606. eCollection 2022. Acta Cir Bras. 2022. PMID: 36074399 Free PMC article.
-
Ulinastatin alleviates early brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting necroptosis and neuroinflammation via MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway.Acta Cir Bras. 2022 May 13;37(3):e370301. doi: 10.1590/acb370301. eCollection 2022. Acta Cir Bras. 2022. PMID: 35584533 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine alleviates early brain injury following traumatic brain injury by inhibiting autophagy and neuroinflammation through the ROS/Nrf2 signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Sep;24(3):661. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12300. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34278508 Free PMC article.
-
Supplement and nutraceutical therapy in traumatic brain injury.Nutr Neurosci. 2025 Jun;28(6):709-743. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2024.2404782. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Nutr Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40440029 Review.
-
Psychedelics for acquired brain injury: a review of molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Mar;29(3):671-685. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02360-0. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38177350 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of ulinastatin therapy in deep vein thrombosis prevention after brain tumor surgery: A single-center randomized controlled trial.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Nov 6;11(31):7583-7592. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i31.7583. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 38078125 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Analysis of transcriptome characteristics of UTI therapy for cerebral injury after CA/ROSC based on RNA-seq technique.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Jun;25(6):715-722. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.61990.13722. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35949311 Free PMC article.
-
Ulinastatin for the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Sep 1;25(1):629. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04239-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40890662 Free PMC article.
-
Ulinastatin Alleviates Repetitive Ketamine Exposure-Evoked Cognitive Impairment in Adolescent Mice.Neural Plast. 2022 Dec 12;2022:6168284. doi: 10.1155/2022/6168284. eCollection 2022. Neural Plast. 2022. PMID: 36545238 Free PMC article.
-
Traumatic brain injury: Mechanisms, manifestations, and visual sequelae.Front Neurosci. 2023 Feb 23;17:1090672. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1090672. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36908792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nichol A, French C, Little L, Haddad S, Presneill J, Arabi Y, Bailey M, Cooper DJ, Duranteau J, Huet O, Mak A, McArthur C, Pettilä V, Skrifvars M, Vallance S, Varma D, Wills J, Bellomo R. Erythropoietin in traumatic brain injury (EPO-TBI): A double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;386(10012):2499–2506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00386-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hutchinson PJ, Kolias AG, Timofeev IS, Corteen EA, Czosnyka M, Timothy J, Anderson I, Bulters DO, Belli A, Eynon CA, Wadley J, Mendelow AD, Mitchell PM, Wilson MH, Critchley G, Sahuquillo J, Unterberg A, Servadei F, Teasdale GM, Pickard JD, Menon DK, Murray GD, Kirkpatrick PJ. Trial of Decompressive Craniectomy for Traumatic Intracranial Hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(12):1119–1130. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1605215. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

