Multimodal MRI examination of structural and functional brain changes in older women with breast cancer in the first year of antiestrogen hormonal therapy
- PMID: 35476252
- PMCID: PMC9255382
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-022-06597-1
Multimodal MRI examination of structural and functional brain changes in older women with breast cancer in the first year of antiestrogen hormonal therapy
Abstract
Purpose: Cancer patients are concerned about treatment-related cognitive problems. We examined effects of antiestrogen hormonal therapy on brain imaging metrics in older women with breast cancer.
Methods: Women aged 60 + treated with hormonal therapy only and matched non-cancer controls (n = 29/group) completed MRI and objective and self-reported cognitive assessment at pre-treatment/enrollment and 12 months later. Gray matter was examined using voxel-based morphometry (VBM), FreeSurfer, and brain age calculations. Functional MRI (fMRI) assessed working memory-related activation. Analyses examined cross-sectional and longitudinal differences and tested associations between brain metrics, cognition, and days on hormonal therapy.
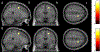
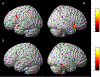
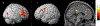
Results: The cancer group showed regional reductions over 12 months in frontal, temporal, and parietal gray matter on VBM, reduced FreeSurfer cortical thickness in prefrontal, parietal, and insular regions, and increased working memory-related fMRI activation in frontal, cingulate, and visual association cortex. Controls showed only reductions in fusiform gyrus on VBM and FreeSurfer temporal and parietal cortex thickness. Women with breast cancer showed higher estimated brain age and lower regional gray matter volume than controls at both time points. The cancer group showed a trend toward lower performance in attention, processing speed, and executive function at follow-up. There were no significant associations between brain imaging metrics and cognition or days on hormonal therapy.
Conclusion: Older women with breast cancer showed brain changes in the first year of hormonal therapy. Increased brain activation during working memory processing may be a sign of functional compensation for treatment-related structural changes. This hypothesis should be tested in larger samples over longer time periods.
Gov identifier: NCT03451383.
Keywords: Antiestrogen hormonal therapy; Breast cancer; Cognition; Multimodal MRI; Neuroimaging; Older women.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Statements & Declarations
Competing Interests: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
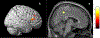
References
-
- Noone AM, Howlader N, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA, eds (based on November 2017 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2018) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2015. National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD
-
- American Cancer Society; (2017) Breast Cancer Facts and Figures 2017–2018. American Cancer Society, Inc., Atlanta
-
- Burstein HJ, Lacchetti C, Anderson H, Buchholz TA, Davidson NE, Gelmon KA, Giordano SH, Hudis CA, Solky AJ, Stearns V, Winer EP, Griggs JJ (2019) Adjuvant endocrine therapy for women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: ASCO clinical practice guideline focused update. J Clin Oncol 37:423–438. 10.1200/jco.18.01160 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Runowicz CD, Leach CR, Henry NL, Henry KS, Mackey HT, Cowens-Alvarado RL, Cannady RS, Pratt-Chapman ML, Edge SB, Jacobs LA, Hurria A, Marks LB, LaMonte SJ, Warner E, Lyman GH, Ganz PA (2016) American Cancer Society/American Society of Clinical Oncology breast cancer survivorship care guideline. CA Cancer J Clin 66:43–73. 10.3322/caac.21319 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U54 CA137788/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244673/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG068086/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM121176/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA132378/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG068193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197289/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA172119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA241337/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA082709/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

