Emerging proteoglycans and proteoglycan-targeted therapies in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 35476502
- PMCID: PMC9169851
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00086.2022
Emerging proteoglycans and proteoglycan-targeted therapies in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
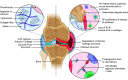
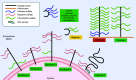
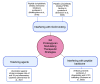
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the joints and damage to the cartilage and bone. The pathogenesis of RA is characterized in many patients by the presence of antibodies against citrullinated proteins. Proteoglycans are key structural elements of extracellular matrix in the joint articular cartilage and synovium and are secreted as lubricants in the synovial fluid. Alterations of proteoglycans contribute to RA pathogenesis. Proteoglycans such as aggrecan can be citrullinated and become potential targets of the rheumatoid autoimmune response. Proteoglycans are also upregulated in RA joints and/or undergo alterations of their regulatory functions over cytokines and chemokines, which promotes inflammation and bone damage. Recent studies have aimed to not only clarify these mechanisms but also develop novel proteoglycan-modulating therapeutics. These include agents altering the function and signaling of proteoglycans as well as tolerizing agents targeting citrullinated aggrecan. This mini-review summarizes the most recent findings regarding the dysregulation of proteoglycans that contributes to RA pathogenesis and the potential for proteoglycan-modulating agents to improve upon current RA therapy.
Keywords: aggrecan; citrullination; proteoglycans; rheumatoid arthritis; syndecan.
Conflict of interest statement
N.B. has a relationship with Knoubis Bio, Inc., which consists of being a scientific founder with equity and interim officer of the company. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California-San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
This article is part of the special collection “Deciphering the Role of Proteoglycans and Glycosaminoglycans in Health and Disease.” Liliana Schaefer, MD, served as Guest Editor of this collection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune Recognition of Citrullinated Proteoglycan Aggrecan Epitopes in Mice with Proteoglycan-Induced Arthritis and in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 28;11(7):e0160284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160284. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27466816 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Localization of Citrullinated Proteoglycan Aggrecan in Human Articular Cartilage.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 4;11(3):e0150784. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150784. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26943656 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors to cartilage proteoglycan and collagen turnover and inflammation as revealed by analyses of synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Nov;44(11):2503-11. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200111)44:11<2503::aid-art430>3.0.co;2-p. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. PMID: 11710706
-
Wnt signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis, with special emphasis on the different roles in synovial inflammation and bone remodeling.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2069-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23602936 Review.
-
Proteoglycan-induced arthritis: immune regulation, cellular mechanisms, and genetics.Crit Rev Immunol. 2003;23(3):199-250. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v23.i3.20. Crit Rev Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14584879 Review.
Cited by
-
Norisoboldine Reduces Arthritis Severity by Attenuating Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Extracellular Matrix Degradation in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Nov 15;17:8839-8852. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S476824. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39564548 Free PMC article.
-
Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 6 in Cardiovascular Biology and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 3;23(21):13429. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113429. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence of Disruption in Neural Regeneration in Dry Eye Secondary to Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 19;24(8):7514. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087514. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108693 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with Sinomenine and related formulations based on different administration routes.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Aug 6;16:1613679. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1613679. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40843369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Composing On-Program Triggers and On-Demand Stimuli into Biosensor Drug Carriers in Drug Delivery Systems for Programmable Arthritis Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 27;15(11):1330. doi: 10.3390/ph15111330. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-AR066053/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)
- P30 AR073761/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007752/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-GM007752/HHS | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 AR066053/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

