Nonlesional lupus skin contributes to inflammatory education of myeloid cells and primes for cutaneous inflammation
- PMID: 35476593
- PMCID: PMC9169615
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn2263
Nonlesional lupus skin contributes to inflammatory education of myeloid cells and primes for cutaneous inflammation
Abstract
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) is a disfiguring and poorly understood condition frequently associated with systemic lupus. Previous studies suggest that nonlesional keratinocytes play a role in disease predisposition, but this has not been investigated in a comprehensive manner or in the context of other cell populations. To investigate CLE immunopathogenesis, normal-appearing skin, lesional skin, and circulating immune cells from lupus patients were analyzed via integrated single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial RNA sequencing. We demonstrate that normal-appearing skin of patients with lupus represents a type I interferon-rich, prelesional environment that skews gene transcription in all major skin cell types and markedly distorts predicted cell-cell communication networks. We also show that lupus-enriched CD16+ dendritic cells undergo robust interferon education in the skin, thereby gaining proinflammatory phenotypes. Together, our data provide a comprehensive characterization of lesional and nonlesional skin in lupus and suggest a role for skin education of CD16+ dendritic cells in CLE pathogenesis.
Figures
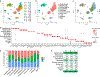


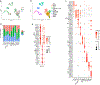

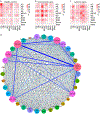


Comment in
-
Keratinocytes: From passive targets to active mediators of systemic autoimmunity.Sci Transl Med. 2022 Apr 27;14(642):eabo3961. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abo3961. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Sci Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35476596
-
Skin inflammation precedes lesions in cutaneous lupus erythematosus.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Jul;18(7):364. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00795-3. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35610364 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chasset F, Arnaud L, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Zahr N, Bessis D, Frances C, The effect of increasing the dose of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in patients with refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE): An open-label prospective pilot study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, (2016). - PubMed
-
- Sarkar MK, Hile GA, Tsoi LC, Xing X, Liu J, Liang Y, Berthier CC, Swindell WR, Patrick MT, Shao S, Tsou PS, Uppala R, Beamer MA, Srivastava A, Bielas SL, Harms PW, Getsios S, Elder JT, Voorhees JJ, Gudjonsson JE, Kahlenberg JM, Photosensitivity and type I IFN responses in cutaneous lupus are driven by epidermal-derived interferon kappa. Ann Rheum Dis 77, 1653–1664 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Der E, Suryawanshi H, Morozov P, Kustagi M, Goilav B, Ranabothu S, Izmirly P, Clancy R, Belmont HM, Koenigsberg M, Mokrzycki M, Rominieki H, Graham JA, Rocca JP, Bornkamp N, Jordan N, Schulte E, Wu M, Pullman J, Slowikowski K, Raychaudhuri S, Guthridge J, James J, Buyon J, Tuschl T, Putterman C, A. Accelerating Medicines Partnership Rheumatoid, C. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Tubular cell and keratinocyte single-cell transcriptomics applied to lupus nephritis reveal type I IFN and fibrosis relevant pathways. Nat Immunol 20, 915–927 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR073196/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130025/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020053/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR040312/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR076975/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069071/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR080594/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR071384/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI022553/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR074302/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR060802/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR078251/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR075043/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR072129/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016042/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

